Mexico
Template:Pp-sock Coordinates: 23°N 102°W / 23°N 102°W
United Mexican States Estados Unidos Mexicanos (Spanish) | |
|---|---|
| Motto: Template:Native phrase ("The Homeland is First") | |
| Anthem: Himno Nacional Mexicano ("Mexican National Anthem") | |
| Capital and largest city | Mexico City 19°26′N 99°8′W / 19.433°N 99.133°W |
| Official languages |
|
| Recognized regional languages | Spanish and 68 Amerindian languages[a] |
| National language | Spanish (de facto)[b] |
| Ethnic groups | See below |
| Religion (2022)[1] |
|
| Demonym(s) | Mexican |
| Government | Federal presidential Template:Raise |
| Andrés Manuel López Obrador | |
| Alejandro Armenta Mier | |
| Santiago Creel | |
| Norma Lucía Piña Hernández | |
| Legislature | Congress |
| Senate | |
| Chamber of Deputies | |
| Independence from Spain | |
• Declared | 16 September 1810 |
| 27 September 1821 | |
| 28 December 1836 | |
| 4 October 1824 | |
| 5 February 1857 | |
| 5 February 1917 | |
| Area | |
• Total | 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi) (13th) |
• Water (%) | 1.58 (as of 2015)[2] |
| Population | |
• 2022 estimate | 129,150,971[3] (10th) |
• 2020 census | 126,014,024[4] (10th) |
• Density | 61/km2 (158.0/sq mi) (142nd) |
| GDP (PPP) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| GDP (nominal) | 2022 estimate |
• Total | |
• Per capita | |
| Gini (2018) | medium |
| HDI (2021) | high · 86th |
| Currency | Mexican peso (MXN) |
| Time zone | UTC−8 to −5 (See Time in Mexico) |
• Summer (DST) | UTC−7 to −5 (varies) |
| Driving side | right |
| Calling code | +52 |
| ISO 3166 code | MX |
| Internet TLD | .mx |
Mexico (Spanish: México),[a][b] officially the United Mexican States,[c] is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico.[11] Mexico covers 1,972,550 km2 (761,610 sq mi),[12] making it the world's 13th-largest country by area; with a population of over 126 million, it is the 10th-most-populous country and has the most Spanish speakers.[4] Mexico is organized as a federal republic comprising 31 states and Mexico City, its capital. Other major urban areas include Monterrey, Guadalajara, Puebla, Toluca, Tijuana, Ciudad Juárez, and León.[13]
Human presence in Pre-Columbian Mexico goes back to 8,000 BCE and it went to become one of the world's six cradles of civilization. In particular, the Mesoamerican region was home to many intertwined civilizations, including the Olmec, Maya, Zapotec, Teotihuacan, and Purepecha. Last were the Aztecs, who dominated the region in the century before European contact. In 1521, the Spanish Empire and its indigenous allies conquered the Aztec Empire from its capital Tenochtitlan (now Mexico City), establishing the colony of New Spain.[14] Over the next three centuries, Spain and the Catholic Church played an important role, expanding the territory, enforcing Christianity and spreading the Spanish language throughout.[15] With the discovery of rich deposits of silver in Zacatecas and Guanajuato, New Spain soon became one of the most important mining centers worldwide. Wealth coming from Asia and the New World contributed to Spain's status as a major world power for the next centuries, and brought about a price revolution in Western Europe.[16] The colonial order came to an end in the early nineteenth century with the War of Independence against Spain.
Mexico's early history as an independent nation state was marked by political and socioeconomic upheaval, both domestically and in foreign affairs. The Federal Republic of Central America shortly seceded the country. Then two invasions by foreign powers took place: first, by the United States as a consequence of the Texas Revolt by American settlers, which led to the Mexican–American War and huge territorial losses in 1848.[17] After the introduction of liberal reforms in the Constitution of 1857, conservatives reacted with the war of Reform and prompted France to invade the country and install an Empire, against the Republican resistance led by liberal President Benito Juárez, which emerged victorious. The last decades of the 19th century were dominated by the dictatorship of Porfirio Díaz, who sought to modernize Mexico and restore order.[18] However, the Porfiriato era led to great social unrest and ended with the outbreak in 1910 of the decade-long Mexican Revolution (civil war). This conflict led to profound changes in Mexican society, including the proclamation of the 1917 Constitution, which remains in effect to this day. The remaining war generals ruled as a succession of presidents until the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI) emerged in 1929. The PRI governed Mexico for the next 70 years, first under a set of paternalistic developmental policies of considerable economic success. During World War II Mexico also played an important role for the Allied war effort.[19][20] Nonetheless, the PRI regime resorted to repression and electoral fraud to maintain power, and moved the country to a more US-aligned neoliberal economic policy during the late 20th century. This culminated with the signing of the North American Free Trade Agreement in 1994, which caused a major indigenous rebellion in the state of Chiapas. PRI lost the presidency for the first time in 2000, against the conservative party (PAN).
Mexico has the world's 15th-largest economy by nominal GDP and the 11th-largest by PPP, with the United States being its largest economic partner. As a newly industrialized[21] and developing country ranking 86th, high in the Human Development Index, its large economy and population, cultural influence, and steady democratization make Mexico a regional and middle power[22][23][24] which is also identified as an emerging power by several analysts.[25][26][27][28] Mexico ranks first in the Americas and seventh in the world for the number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites.[29] It is also one of the world's 17 megadiverse countries, ranking fifth in natural biodiversity.[30] Mexico's rich cultural and biological heritage, as well as varied climate and geography, makes it a major tourist destination: as of 2018, it was the sixth most-visited country in the world, with 39 million international arrivals.[31] However, the country continues to struggle with social inequality, poverty and extensive crime. It ranks poorly on the Global Peace Index,[32] due in large part to ongoing conflict between drug trafficking syndicates, which violently compete for the US drug market and trade routes. This "drug war" has led to over 120,000 deaths since 2006.[33] Mexico is a member of United Nations, the G20, the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), the World Trade Organization (WTO), the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation forum, the Organization of American States, Community of Latin American and Caribbean States, and the Organization of Ibero-American States.
Etymology edit
Mēxihco is the Nahuatl term for the heartland of the Aztec Empire, namely the Valley of Mexico and surrounding territories, with its people being known as the Mexica. The terms are plainly linked; it is generally believed that the toponym for the valley was the origin of the primary ethnonym for the Aztec Triple Alliance, but it may have been the other way around.[34] In the colonial era (1521–1821) Mexico was called New Spain. In the eighteenth century, this central region became the Intendency of Mexico, during the reorganization of the empire, the Bourbon Reforms. After New Spain achieved independence from the Spanish Empire in 1821 and became a sovereign state, the territory came to be known as the State of Mexico, with the new country being named after its capital: Mexico City, which itself was founded in 1524 on the site of the ancient Mexica capital of Tenochtitlan. The official name of the country has changed as the form of government has changed. The declaration of independence signed on 6 November 1813 by the deputies of the Congress of Anáhuac called the territory América Septentrional (Northern America); the 1821 Plan of Iguala also used América Septentrional. On two occasions (1821–1823 and 1863–1867), the country was known as Imperio Mexicano (Mexican Empire). All three federal constitutions (1824, 1857 and 1917, the current constitution) used the name Estados Unidos Mexicanos[35]—or the variant Estados-Unidos Mexicanos,[36] all of which have been translated as "United Mexican States". The phrase República Mexicana, "Mexican Republic", was used in the 1836 Constitutional Laws.[37]
History edit
Indigenous civilizations before European contact (pre-1519) edit
The prehistory of Mexico stretches back millennia. The earliest human artifacts in Mexico are chips of stone tools found near campfire remains in the Valley of Mexico and radiocarbon-dated to circa 10,000 years ago.[38] Mexico is the site of the domestication of maize, tomato, and beans, which produced an agricultural surplus. This enabled the transition from paleo-Indian hunter-gatherers to sedentary agricultural villages beginning around 5000 BCE.[39] In the subsequent formative eras, maize cultivation and cultural traits such as a mythological and religious complex, and a vigesimal (base 20) numeric system, were diffused from the Mexican cultures to the rest of the Mesoamerican culture area.[40] In this period, villages became more dense in terms of population, becoming socially stratified with an artisan class, and developing into chiefdoms. The most powerful rulers had religious and political power, organizing the construction of large ceremonial centers.[41]
The earliest complex civilization in Mexico was the Olmec culture, which flourished on the Gulf Coast from around 1500 BCE. Olmec cultural traits diffused through Mexico into other formative-era cultures in Chiapas, Oaxaca and the Valley of Mexico. The formative period saw the spread of distinct religious and symbolic traditions, as well as artistic and architectural complexes.[42] The formative-era of Mesoamerica is considered one of the six independent cradles of civilization. In the subsequent pre-classical period, the Maya and Zapotec civilizations developed complex centers at Calakmul and Monte Albán, respectively. During this period the first true Mesoamerican writing systems were developed in the Epi-Olmec and the Zapotec cultures. The Mesoamerican writing tradition reached its height in the Classic Maya Hieroglyphic script. The earliest written histories date from this era. The tradition of writing was important after the Spanish conquest in 1521, with indigenous scribes learning to write their languages in alphabetic letters, while also continuing to create pictorial texts.[43][44]
In Central Mexico, the height of the classic period saw the ascendancy of Teotihuacán, which formed a military and commercial empire whose political influence stretched south into the Maya area as well as north. Teotihuacan, with a population of more than 150,000 people, had some of the largest pyramidal structures in the pre-Columbian Americas.[45] After the collapse of Teotihuacán around 600 AD, competition ensued between several important political centers in central Mexico such as Xochicalco and Cholula. At this time, during the Epi-Classic, Nahua peoples began moving south into Mesoamerica from the North, and became politically and culturally dominant in central Mexico, as they displaced speakers of Oto-Manguean languages. During the early post-classic era (ca. 1000–1519 CE), Central Mexico was dominated by the Toltec culture, Oaxaca by the Mixtec, and the lowland Maya area had important centers at Chichén Itzá and Mayapán. Toward the end of the post-Classic period, the Mexica established dominance, establishing a political and economic empire based in the city of Tenochtitlan (modern Mexico City), extending from central Mexico to the border with Guatemala.[46] Alexander von Humboldt popularized the modern usage of "Aztec" as a collective term applied to all the people linked by trade, custom, religion, and language to the Mexica state and Ēxcān Tlahtōlōyān, the Triple Alliance.[47] In 1843, with the publication of the work of William H. Prescott, it was adopted by most of the world, including 19th-century Mexican scholars who considered it a way to distinguish present-day Mexicans from pre-conquest Mexicans. This usage has been the subject of debate since the late 20th century.[48]
The Aztec empire was an informal or hegemonic empire because it did not exert supreme authority over the conquered territories; it was satisfied with the payment of tributes from them. It was a discontinuous empire because not all dominated territories were connected; for example, the southern peripheral zones of Xoconochco were not in direct contact with the center. The hegemonic nature of the Aztec empire was demonstrated by their restoration of local rulers to their former position after their city-state was conquered. The Aztec did not interfere in local affairs, as long as the tributes were paid.[49] The Aztec of Central Mexico built a tributary empire covering most of central Mexico.[50] The Aztec were noted for practicing human sacrifice on a large scale. Along with this practice, they avoided killing enemies on the battlefield. Their warring casualty rate was far lower than that of their Spanish counterparts, whose principal objective was immediate slaughter during battle.[51] This distinct Mesoamerican cultural tradition of human sacrifice ended gradually with the Spanish conquest in the 16th century. Other Mexican indigenous cultures were conquered and gradually subjected to Spanish colonial rule.[52]
Since the colonial era and through to the twenty-first century, the indigenous roots of Mexican history and culture are essential to Mexican identity. The National Museum of Anthropology in Mexico City is the showcase of the nation's prehispanic glories. Historian Enrique Florescano calls it "a national treasure and a symbol of identity. The museum is the synthesis of an ideological, scientific, and political feat."[53] Mexican Nobel laureate Octavio Paz said of the museum that the "exaltation and glorification of Mexico-Tenochtitlan transforms the Museum of Anthropology into a temple."[54] Mexico pursued international recognition of its prehispanic heritage, and has a large number of UNESCO World Heritage Sites, the largest in the hemisphere. The existence of high indigenous civilization prior to the arrival of Europeans has also had an impact on European thought.[55]
Spanish conquest and colonial era (1519–1821) edit
Although the Spanish Empire had established colonies in the Caribbean starting in 1493, only in the second decade of the sixteenth century did they begin exploring the east coast of Mexico. The Spanish first learned of Mexico during the Juan de Grijalva expedition of 1518. The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire began in February 1519 when Hernán Cortés landed on the Gulf Coast and founded the Spanish city of Veracruz. Around 500 conquistadores, along with horses, cannons, swords, and long guns gave the Spanish some technological advantages over indigenous warriors, but key to the Spanish victory was making strategic alliances with disgruntled indigenous city-states (altepetl) who fought with them against the Aztec Triple Alliance. Also important to the Spanish victory was Cortés's cultural translator, Malinche, a Nahua woman enslaved in the Maya area whom the Spanish acquired as a gift. She quickly learned Spanish and gave strategic advice about how to deal with both indigenous allies and indigenous foes.[56]
The Spanish conquest is well documented from multiple points of view. There are accounts by the Spanish leader Cortés[57] and multiple other Spanish participants, including Bernal Díaz del Castillo.[58][59] There are indigenous accounts in Spanish, Nahuatl, and pictorial narratives by allies of the Spanish, most prominently the Tlaxcalans, as well as Texcocans[60] and Huejotzincans, and the defeated Mexica themselves, recorded in the last volume of Bernardino de Sahagún's General History of the Things of New Spain.[61][62][63]
The 1521 capture of Tenochtitlan and immediate founding of the Spanish capital Mexico City on its ruins was the beginning of a 300-year-long colonial era during which Mexico was known as Nueva España (New Spain). Two factors made Mexico a jewel in the Spanish Empire: the existence of large, hierarchically organized Mesoamerican populations that rendered tribute and performed obligatory labor and the discovery of vast silver deposits in northern Mexico.[64] The Kingdom of New Spain was created from the remnants of the Aztec empire. The two pillars of Spanish rule were the State and the Roman Catholic Church, both under the authority of the Spanish crown. In 1493 the pope had granted sweeping powers to the Spanish monarchy for its overseas empire, with the proviso that the crown spread Christianity in its new realms. In 1524, King Charles I created the Council of the Indies based in Spain to oversee State power its overseas territories; in New Spain the crown established a high court in Mexico City, the Real Audiencia, and then in 1535 created the Viceroyalty of New Spain. The viceroy was highest official of the State. In the religious sphere, the diocese of Mexico was created in 1530 and elevated to the Archdiocese of Mexico in 1546, with the archbishop as the head of the ecclesiastical hierarchy, overseeing Roman Catholic clergy. Castilian Spanish was the language of rulers. The Catholic faith the only one permitted, with non-Catholics (Jews and Protestants) and Catholics (excluding Indians) holding unorthodox views being subject to the Mexican Inquisition, established in 1571.[65]
In the first half-century of Spanish rule, a network of Spanish cities was created, sometimes on pre-Columbian sites where there were dense indigenous populations. The capital Mexico City was and remains the premier city, but other cities founded in the sixteenth century remain important, including Puebla, Guadalajara, Guanajuato, Zacatecas, Oaxaca, and the port of Veracruz. Cities and towns were hubs of civil officials, ecclesiastics, business, Spanish elites, and mixed-race and indigenous artisans and workers. When deposits of silver were discovered in sparsely populated northern Mexico, far from the dense populations of central Mexico, the Spanish secured the region against fiercely resistant indigenous Chichimecas. The Viceroyalty at its greatest extent included the territories of modern Mexico, Central America as far south as Costa Rica, and the western United States. The Viceregal capital Mexico City also administrated the Spanish West Indies (the Caribbean), the Spanish East Indies (that is, the Philippines), and Spanish Florida. In 1819, the Spain signed the Adams-Onís Treaty with the United States, setting New Spain's northern boundary.[66]
The rich deposits of silver, particularly in Zacatecas and Guanajuato, resulted in silver extraction dominating the economy of New Spain. Mexican silver pesos became the first globally used currency. Taxes on silver production became a major source of income for the Spanish monarchy. Other important industries were the agricultural and ranching haciendas and mercantile activities in the main cities and ports.[citation needed] As a result of its trade links with Asia, the rest of the Americas, Africa and Europe and the profound effect of New World silver, central Mexico was one of the first regions to be incorporated into a globalized economy. Being at the crossroads of trade, people and cultures, Mexico City has been called the "first world city".[67] The Nao de China (Manila Galleons) operated for two and a half centuries and connected New Spain with Asia. Silver and the red dye cochineal were shipped from Veracruz to Atlantic ports in the Americas and Spain. Veracruz was also the main port of entry in mainland New Spain for European goods, immigrants from Spain, and African slaves. The Camino Real de Tierra Adentro connected Mexico City with the interior of New Spain.
The population of Mexico was overwhelmingly indigenous and rural during the entire colonial period and beyond, despite the massive decrease in their numbers due to epidemic diseases. Diseases such as smallpox, measles, and others were introduced by Europeans and African slaves, especially in the sixteenth century. The indigenous population stabilized around one to one and a half million individuals in the 17th century from the most commonly accepted five to thirty million pre-contact population.[68] During the three hundred years of the colonial era, Mexico received between 400,000 and 500,000 Europeans,[69] between 200,000 and 250,000 African slaves.[70] and between 40,000 and 120,000 Asians.[71][72]
Under Viceroy Revillagigedo the first comprehensive census was created in 1793, with racial classifications. Although most of its original datasets have reportedly been lost, thus most of what is known about it comes from essays and field investigations made by scholars who had access to the census data and used it as reference for their works such as German scientist Alexander von Humboldt. Europeans ranged from 18% to 22% of New Spain's population, Mestizos from 21% to 25%, Indians from 51% to 61% and Africans were between 6,000 and 10,000. The total population ranged from 3,799,561 to 6,122,354. It is concluded that the population growth trends of whites and mestizos were even, while the percentage of the indigenous population decreased at a rate of 13%–17% per century, mostly due to the latter having higher mortality rates from living in remote locations and being in constant war with the colonists.[73] Independence-era Mexico eliminated the legal basis for the hierarchical system of racial classification, although the racial/ethnic labels continued to be used.
Colonial law with Spanish roots was introduced and attached to native customs creating a hierarchy between local jurisdiction (the Cabildos) and the Spanish Crown. Upper administrative offices were closed to native-born people, even those of pure Spanish blood (criollos). Administration was based on the racial separation. Society was organized in a racial hierarchy, with whites on top, mixed-race persons and blacks in the middle, and indigenous at the bottom. There were formal legal designations of racial categories. The Republic of Spaniards (República de Españoles) comprised European- and American-born Spaniards, mixed-race castas, and black Africans. The Republic of Indians (República de Indios) comprised the indigenous populations, which the Spanish lumped under the term Indian (indio), a Spanish colonial social construct which indigenous groups and individuals rejected as a category. Spaniards were exempt from paying tribute, Spanish men had access to higher education, could hold civil and ecclesiastical offices, were subject to the Inquisition, and liable for military service when the standing military was established in the late eighteenth century. Indigenous paid tribute, but were exempt from the Inquisition, indigenous men were excluded from the priesthood; and exempt from military service. Although the racial system appears fixed and rigid, there was some fluidity within it, and racial domination of whites was not complete.[75] Since the indigenous population of New Spain was so large, there was less labor demand for expensive black slaves than other parts of Spanish America.[76][77] In the late eighteenth century the crown instituted reforms that privileged Iberian-born Spaniards (peninsulares) over American-born (criollos), limiting their access to offices. This discrimination between the two became a sparking point of discontent for white elites in the colony.[78]
The Marian apparition of the Virgin of Guadalupe said to have appeared to the indigenous Juan Diego in 1531 gave impetus to the evangelization of central Mexico.[79][80] The Virgin of Guadalupe became a symbol for American-born Spaniards' (criollos) patriotism, seeking in her a Mexican source of pride, distinct from Spain.[81] The Virgin of Guadalupe was invoked by the insurgents for independence who followed Father Miguel Hidalgo during the War of Independence.[80]
Spanish military forces, sometimes accompanied by native allies, led expeditions to conquer territory or quell rebellions through the colonial era. Notable Amerindian revolts in sporadically populated northern New Spain include the Chichimeca War (1576–1606),[82] Tepehuán Revolt (1616–1620),[83] and the Pueblo Revolt (1680), the Tzeltal Rebellion of 1712 was a regional Maya revolt.[84] Most rebellions were small-scale and local, posing no major threat to the ruling elites.[85] To protect Mexico from the attacks of English, French, and Dutch pirates and protect the Crown's monopoly of revenue, only two ports were open to foreign trade—Veracruz on the Atlantic and Acapulco on the Pacific. Among the best-known pirate attacks are the 1663 Sack of Campeche[86] and 1683 Attack on Veracruz.[87] Of greater concern to the crown was of foreign invasion, especially after Britain seized in 1762 the Spanish ports of Havana, Cuba and Manila, the Philippines in the Seven Years' War. It created a standing military, increased coastal fortifications, and expanded the northern presidios and missions into Alta California. The volatility of the urban poor in Mexico City was evident in the 1692 riot in the Zócalo. The riot over the price of maize escalated to a full-scale attack on the seats of power, with the viceregal palace and the archbishop's residence attacked by the mob.[75]
Independence era (1808–1821) edit
The upheaval in the Spanish Empire that resulted in the independence of most of its New World territories was due to Napoleon Bonaparte's invasion of Spain in 1808. Napoleon forced the abdication of the Spanish monarch Charles IV and imposed of his brother Joseph Bonaparte as the Spanish king. Now with an alien usurper on the Spanish throne, there was a crisis of legitimacy of the monarchy, resulting in various responses in both Spain and Spanish America. In Mexico, elites argued that sovereignty now reverted to "the people" and that town councils (cabildos) were the most representative bodies. American-born Spaniards petitioned the viceroy José de Iturrigaray (1803–08) to convene a junta to determine rule in Mexico in the current political crisis. Although Peninsular-born Spaniards were opposed to the plan, the viceroy called together wealthy landowners, miners, merchants, ecclesiastics, academics, and members of cabildos. They failed to come to agreement, and in the meantime, Peninsular-born Spaniards took the initiative, arresting Iturrigaray and leading creole elites in the capital. The coup ended what could have been a peaceful process toward political autonomy in Mexico. Creoles now sought extralegal means to achieve their political aspirations.[88]
On 16 September 1810, secular priest Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla declared against "bad government" in the small town of Dolores, Guanajuato. This event, known as the Cry of Dolores (Spanish: Grito de Dolores) is commemorated each year, on 16 September, as Mexico's independence day.[89] The first insurgent group was formed by Hidalgo, army captain Ignacio Allende, the militia captain Juan Aldama and the wife of the local magistrate (Corregidor) Josefa Ortiz de Domínguez, known as La Corregidora. Hidalgo's local declaration sparked a huge revolt of the masses, an uncontrollable uprising targeting the persons and property of white elites, whether Peninsular- or American-born. Famously in Guanajuato, elites took refuge in the central grain storage (alhondiga), bringing their treasure, attempted to hold out against Hidalgo's followers, but were slaughtered. In an event emblematic of the war of independence, "Hidalgo's capture of the great silver city of Guanajuato on September 28, 1810, is the most famous single episode of the decade-long insurgency."[90] Hidalgo and some of his soldiers were eventually captured, Hidalgo was defrocked, and they were executed by firing squad in Chihuahua, on 31 July 1811. The heads of the executed rebels were subsequently displayed on the granary. Following Hidalgo's death, Ignacio López Rayón and then by the priest José María Morelos assumed the leadership, occupying key southern cities with the support of Mariano Matamoros and Nicolás Bravo. In 1813 the Congress of Chilpancingo was convened and, on 6 November, signed the "Solemn Act of the Declaration of Independence of Northern America". This Act also called for the abolition of slavery and the system of racial hierarchy, and Roman Catholicism the sole religion. Morelos was captured and executed on 22 December 1815.
In subsequent years, the insurgency was a stalemate, but in 1820 when Spanish liberals seized power in Spain, and Mexican conservatives worried about the imposition of liberal principles overseas, including curtailment of the power of the Catholic Church. Royalist criollo general Agustín de Iturbide was to continue fighting against Vicente Guerrero and insurgents in the south. Instead of attacking Guerrero, Itubide approached Guerrero to join forces to seize power in Mexico. Iturbide issued the Plan of Iguala on 24 February 1821. Sometimes called the Act of Independence, it called for Roman Catholicism as the nation's sole religion; the establishment of a constitutional monarchy; and the equality of those born in Spain and those born in Mexico, the "three guarantees" can be summarized as "religion, independence, and union". All were to be equal citizens in the new sovereign nation, regardless of place of birth or racial category, a requirement that Guerrero, the mixed-race leader of the insurgency, insisted on for his joining with Iturbide. The flag of the newly formed Army of the Three Guarantees has evolved into today's Mexican flag. On 24 August 1821 in incoming Viceroy and Iturbide signed the Treaty of Córdoba and the Declaration of Independence of the Mexican Empire", which recognized the independence of Mexico under the terms of the Plan of Iguala. The Spanish crown repudiated the 1821 treaty and did not formally recognize the independence of Mexico until 1836.
Early Post-Independence (1821–1855) edit
The first 35 years after Mexico's independence were marked by political instability and the changing of the Mexican state from a transient monarchy to a fragile federated republic.[91] There were military coups d'état, foreign invasions, ideological conflict between Conservatives and Liberals, and economic stagnation. Catholicism remained the only permitted religious faith and the Catholic Church as an institution retained its special privileges, prestige, and property, a bulwark of Conservatism. The army, another Conservative-dominated institution, also retained its privileges. Former Royal Army General Agustín de Iturbide, became regent, as newly independent Mexico sought a constitutional monarch from Europe. When no member of a European royal house desired the position, Iturbide himself was declared Emperor Agustín I. The young and weak United States was the first country to recognize Mexico's independence, sending an ambassador to the court of the emperor and sending a message to Europe via the Monroe Doctrine not to intervene in Mexico. The emperor's rule was short (1822–1823) and he was overthrown by army officers in the Plan of Casa Mata.[92]
After the forced abdication of the monarch, the First Mexican Republic was established. In 1824, a constitution of a federated republic was promulgated and former insurgent General Guadalupe Victoria became the first president of the republic, the first of many army generals to hold the presidency of Mexico. Central America, including Chiapas, left the union. In 1829, former insurgent general and fierce Liberal Vicente Guerrero, a signatory of the Plan de Iguala that achieved independence, became president in a disputed election. During his short term in office, April to December 1829, he abolished slavery. As a visibly mixed-race man of modest origins, Guerrero was seen by white political elites as an interloper.[93] His Conservative vice president, former Royalist General Anastasio Bustamante, led a coup against him and Guerrero was judicially murdered.[94] There was constant strife between the Liberals (also known as Federalists), who were supporters of a federal form of decentralized government, and their political rivals, the Conservatives (also known as Centralists), who proposed a hierarchical form of government.
Mexico's ability to maintain its independence and establish a viable government was in question. Spain attempted to reconquer its former colony during the 1820s, but eventually recognized its independence. France attempted to recoup losses it claimed for its citizens during Mexico's unrest and blockaded the Gulf Coast during the so-called Pastry War of 1838–1839.[95] General Antonio López de Santa Anna emerged as a national hero because of his role in both these conflicts; he lost a leg in combat during the Pastry War, which he used for political purposes to show his sacrifice for the nation. Santa Anna came to dominate the politics for the next 25 years, often known as the "Age of Santa Anna", until his own overthrow in 1855.[96]
Mexico also contended with indigenous groups which controlled territory that Mexico claimed in the north. The Comanche controlled a huge territory in the sparsely populated region of central and northern Texas.[97] Wanting to stabilize and develop the frontier, the Mexican government encouraged Anglo-American immigration into present-day Texas, a region that bordered that United States. There were few settlers from central Mexico moving to this remote and hostile territory. Mexico by law was a Catholic country; the Anglo Americans were primarily Protestant English speakers from the southern United States. Some brought their black slaves, which after 1829 was contrary to Mexican law. In 1835, Santa Anna sought to centralize government rule in Mexico, suspending the 1824 constitution and promulgating the Seven Laws, which placed power in his hands. As a result, civil war spread across the country. Three new governments declared independence: the Republic of Texas, the Republic of the Rio Grande and the Republic of Yucatán.[98]: 129–137 The largest blow to Mexico was the U.S. invasion of Mexico in 1846 in the Mexican–American War. Mexico lost much of its sparsely populated northern territory, sealed in the 1848 Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo. Despite that disastrous loss, Conservative Santa Anna returned to the presidency yet again and then was ousted and exiled in the Liberal Revolution of Ayutla.
Liberal era (1855–1911) edit
The overthrow of Santa Anna and the establishment of a civilian government by Liberals allowed them to enact laws that they considered vital for Mexico's economic development. It was a prelude to more civil wars and yet another foreign invasion. The Liberal Reform attempted to modernize Mexico's economy and institutions along liberal principles. They promulgated a new Constitution of 1857, separating Church and State, stripping the Conservative institutions of the Church and the military of their special privileges (fueros); mandating the sale of Church-owned property and sale of indigenous community lands, and secularizing education.[99] Conservatives revolted, touching off civil war between rival Liberal and Conservative governments (1858–61).
The Liberals defeated the Conservative army on the battlefield, but Conservatives sought another solution to gain power via foreign intervention by the French. Mexican conservatives asked Emperor Napoleon III to place a European monarch as head of state in Mexico. The French Army defeated the Mexican Army and placed Maximilian Hapsburg on the newly established throne of Mexico, supported by Mexican Conservatives and propped up by the French Army. The Liberal republic under Benito Juárez was basically a government in internal exile, but with the end of the Civil War in the U.S. in April 1865, that government began aiding the Mexican Republic. Two years later, the French Army withdrew its support, Maximilian remained in Mexico rather than return to Europe. Republican forces captured him and he was executed in Querétaro, along with two Conservative Mexican generals. The "Restored Republic" saw the return of Juárez, who was "the personification of the embattled republic,"[100] as president.
The Conservatives had been not only defeated militarily, but also discredited politically for their collaboration with the French invaders. Liberalism became synonymous with patriotism.[101] The Mexican Army that had its roots in the colonial royal army and then the army of the early republic was destroyed. New military leaders had emerged from the War of the Reform and the conflict with the French, most notably Porfirio Díaz, a hero of the Cinco de Mayo, who now sought civilian power. Juárez won re-election in 1867, but was challenged by Díaz, who criticized him for running for re-election. Díaz then rebelled, crushed by Juárez. Having won re-election, Juárez died in office of natural causes in July 1872, and Liberal Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada became president, declaring a "religion of state" for rule of law, peace, and order. When Lerdo ran for re-election, Díaz rebelled against the civilian president, issuing the Plan of Tuxtepec. Díaz had more support and waged guerrilla warfare against Lerdo. On the verge of Díaz's victory on the battlefield, Lerdo fled from office, going into exile.[102]
After the turmoil in Mexico from 1810 to 1876, the 35-year rule of Liberal General Porfirio Díaz (r.1876–1911) allowed Mexico to rapidly modernize in a period characterized as one of "order and progress". The Porfiriato was characterized by economic stability and growth, significant foreign investment and influence, an expansion of the railroad network and telecommunications, and investments in the arts and sciences.[103] The period was also marked by economic inequality and political repression. Díaz knew the potential for army rebellions, and systematically downsized the expenditure for the force, rather expanding the rural police force under direct control of the president. Díaz did not provoke the Catholic Church, coming to a modus vivendi with it; but he did not remove the anticlerical articles from the 1857 Constitution. From the late nineteenth century, Protestants began to make inroads into overwhelmingly Catholic Mexico.
The government encouraged British and U.S. investment. Commercial agriculture developed in northern Mexico, with many investors from the U.S. acquiring vast ranching estates and expanding irrigated cultivation of crops. The Mexican government ordered a survey of land with the aim of selling it for development. In this period, many indigenous communities lost their lands and the men became landless wage earners on large landed enterprises (haciendas).[104] British and U.S. investors developed extractive mining of copper, lead, and other minerals, as well as petroleum on the Gulf Coast. Changes in Mexican law allowed for private enterprises to own the subsoil rights of land, rather than continuing the colonial law that gave all subsoil rights to the State. An industrial manufacturing sector also developed, particularly in textiles. At the same time, new enterprises gave rise to an industrial work force, which began organizing to gain labor rights and protections.
Díaz ruled with a group of advisors that became known as the científicos ("scientists").[105] The most influential científico was Secretary of Finance José Yves Limantour.[106] The Porfirian regime was influenced by positivism.[107] They rejected theology and idealism in favor of scientific methods being applied towards national development. An integral aspect of the liberal project was secular education. The Díaz government led a protracted conflict against the Yaqui that culminated with the forced relocation of thousands of Yaqui to Yucatán and Oaxaca. Díaz's long success did not include planning for a political transition beyond his own presidency. He made no attempt, however, to establish a family dynasty, naming no relative as his successor. As the centennial of independence approached, Díaz gave an interview where he said he was not going to run in the 1910 elections, when he would be 80. Political opposition had been suppressed and there were few avenues for a new generation of leaders. But his announcement set off a frenzy of political activity, including the unlikely candidacy of the scion of a rich landowning family, Francisco I. Madero. Madero won a surprising amount of political support when Díaz changed his mind and ran in the election, jailing Madero. The September centennial celebration of independence was the last celebration of the Porfiriato. The Mexican Revolution starting in 1910 saw a decade of civil war, the "wind that swept Mexico."[108]
Mexican Revolution (1910–1920) edit
The Mexican Revolution was a decade-long transformational conflict in Mexico, with consequences to this day.[109] It began with scattered uprisings against President Díaz after the fraudulent 1910 election, his resignation in May 1911, demobilization of rebel forces and an interim presidency of a member of the old guard, and the democratic election of a rich, civilian landowner, Francisco I. Madero in fall 1911. In February 1913, a military coup d'état overthrew Madero's government, with the support of the U.S., resulting in Madero's murder by agents of Federal Army General Victoriano Huerta. A coalition of anti-Huerta forces in the North, the Constitutional Army led by Governor of Coahuila Venustiano Carranza, and a peasant army in the South under Emiliano Zapata defeated the Federal Army.[110]
In 1914, that army was dissolved as an institution, leaving only revolutionary forces. Following the revolutionaries' victory against Huerta, they sought to broker a peaceful political solution, but the coalition splintered, plunging Mexico again into a civil war. Constitutionalist general Pancho Villa, commander of the Division of the North, broke with Carranza and allied with Zapata. Carranza's best general Alvaro Obregón defeated Villa, his former comrade-in-arms in the Battle of Celaya in 1915, and Villa's northern forces melted away. Zapata's forces in the south reverted to guerrilla warfare. Carranza became the de facto head of Mexico, and the U.S. recognized his government.[110]
In 1916, the winners met at a constitutional convention to draft the Constitution of 1917, which was ratified in February 1917. The Constitution empowered the government to expropriate resources including land (Article 27); gave rights to labor (Article 123); and strengthened anticlerical provisions of the 1857 Constitution.[110] With amendments, it remains the governing document of Mexico. It is estimated that the war killed 900,000 of the 1910 population of 15 million.[111][112] Although often viewed as an internal conflict, the revolution had significant international elements.[113] During the Revolution, the U.S. played a significant role with the Republican administration of Taft having supported the Huerta coup against Madero, but when Democrat Woodrow Wilson was inaugurated as president in March 1913, Wilson refused to recognize Huerta's regime and allowed arms sales to the Constitutionalists. Wilson ordered troops to occupy the strategic port of Veracruz in 1914, which was lifted.[114]
After Pancho Villa was defeated by revolutionary forces in 1915, he led an incursion raid into Columbus, New Mexico, prompting the U.S. to send 10,000 troops led by General John J. Pershing in an unsuccessful attempt to capture Villa. Carranza pushed back against U.S. troops being in northern Mexico. The expeditionary forces withdrew as the U.S. entered World War I.[115] Germany attempted to get Mexico to side with it, sending a coded telegram in 1917 to incite war between the U.S. and Mexico, with Mexico to regain the territory it lost in the Mexican-American War.[116] Mexico remained neutral in the conflict.
Consolidating power, President Carranza had peasant-leader Emiliano Zapata assassinated in 1919. Carranza had gained support of the peasantry during the Revolution, but once in power he did little to institute land reform, which had motivated many to fight in the Revolution. Carranza in fact returned some confiscated land to their original owners. President Carranza's best general, Obregón, served briefly in his administration, but returned to his home state of Sonora to position himself to run in the 1920 presidential election. Since Carranza could not run for re-election, he chose a civilian, political and revolutionary no-body to succeed him, intending to remain the power behind the presidency. Obregón and two other Sonoran revolutionary generals drew up the Plan of Agua Prieta, overthrowing Carranza, who died fleeing Mexico City in 1920. General Adolfo de la Huerta became interim president, followed the election of General Álvaro Obregón.
Political consolidation and one-party rule (1920–2000) edit
The first quarter-century of the post-revolutionary period (1920–1946) was characterized by revolutionary generals serving as Presidents of Mexico, including Álvaro Obregón (1920–24), Plutarco Elías Calles (1924–28), Lázaro Cárdenas (1934–40), and Manuel Avila Camacho (1940–46). Since 1946, no member of the military has been President of Mexico. The post-revolutionary project of the Mexican government sought to bring order to the country, end military intervention in politics, and create organizations of interest groups. Workers, peasants, urban office workers, and even the army for a short period were incorporated as sectors of the single party that dominated Mexican politics from its founding in 1929. Obregón instigated land reform and strengthened the power of organized labor. He gained recognition from the United States and took steps to settle claims with companies and individuals that lost property during the Revolution. He imposed his fellow former Sonoran revolutionary general, Calles, as his successor, prompting an unsuccessful military revolt. As president, Calles provoked a major conflict with the Catholic Church and Catholic guerrilla armies when he strictly enforced anticlerical articles of the 1917 Constitution. The Church-State conflict was mediated and ended with the aid of the U.S. Ambassador to Mexico and ended with an agreement between the parties in conflict, by means of which the respective fields of action were defined. Although the constitution prohibited reelection of the president, Obregón wished to run again and the constitution was amended to allow non-consecutive re-election. Obregón won the 1928 elections, but was assassinated by a Catholic zealot, causing a political crisis of succession. Calles could not become president again, since he has just ended his term. He sought to set up a structure to manage presidential succession, founding the party that was to dominate Mexico until the late twentieth century. Calles declared that the Revolution had moved from caudillismo (rule by strongmen) to the era institucional (institutional era).[117]
Despite not holding the presidency, Calles remained the key political figure during the period known as the Maximato (1929–1934). The Maximato ended during the presidency of Lázaro Cárdenas, who expelled Calles from the country and implemented many economic and social reforms. This included the Mexican oil expropriation in March 1938, which nationalized the U.S. and Anglo-Dutch oil company known as the Mexican Eagle Petroleum Company. This movement would result in the creation of the state-owned Mexican oil company Pemex. This sparked a diplomatic crisis with the countries whose citizens had lost businesses by Cárdenas's radical measure, but since then the company has played an important role in the economic development of Mexico. Cárdenas's successor, Manuel Ávila Camacho (1940–1946) was more moderate, and relations between the U.S. and Mexico vastly improved during World War II, when Mexico was a significant ally, providing manpower and materiel to aid the war effort. From 1946 the election of Miguel Alemán, the first civilian president in the post-revolutionary period, Mexico embarked on an aggressive program of economic development, known as the Mexican miracle, which was characterized by industrialization, urbanization, and the increase of inequality in Mexico between urban and rural areas.[118]
With robust economic growth, Mexico sought to showcase it to the world by hosting the 1968 Summer Olympics. The government poured huge resources into building new facilities. At the same time, there was political unrest by university students and others with those expenditures, while their own circumstances were difficult. Demonstrations in central Mexico City went on for weeks before the planned opening of the games, with the government of Gustavo Díaz Ordaz cracking down. The culmination was the Tlatelolco Massacre,[119] which claimed the lives of around 300 protesters based on conservative estimates and perhaps as many as 800.[120] Although the economy continued to flourish for some, social inequality remained a factor of discontent. PRI rule became increasingly authoritarian and at times oppressive in what is now referred to as the Mexican Dirty War.[121]
Luis Echeverría, Minister of the Interior under Díaz Ordaz, carrying out the repression during the Olympics, was elected president in 1970. His government had to contend with mistrust of Mexicans and increasing economic problems. He instituted some with electoral reforms.[122][123] Echeverría chose José López Portillo as his successor in 1976. Economic problems worsened in his early term, then massive reserves of petroleum were located off Mexico's Gulf Coast. Pemex did not have the capacity to develop these reserves itself, and brought in foreign firms. Oil prices had been high because of OPEC's lock on oil production, and López Portilla borrowed money from foreign banks for current spending to fund social programs. Those foreign banks were happy to lend to Mexico because the oil reserves were enormous and future revenues were collateral for loans denominated in U.S. dollars. When the price of oil dropped, Mexico's economy collapsed in the 1982 Crisis. Interest rates soared, the peso devalued, and unable to pay loans, the government defaulted on its debt. President Miguel de la Madrid (1982–88) resorted to currency devaluations which in turn sparked inflation.
In the 1980s the first cracks emerged in the PRI's complete political dominance. In Baja California, the PAN candidate was elected as governor. When De la Madrid chose Carlos Salinas de Gortari as the candidate for the PRI, and therefore a foregone presidential victor, Cuauhtémoc Cárdenas, son of former President Lázaro Cárdenas, broke with the PRI and challenged Salinas in the 1988 elections. In 1988 there was massive electoral fraud, with results showing that Salinas had won the election by the narrowest percentage ever. There were massive protests in Mexico City to the stolen election. Salinas took the oath of office on 1 December 1988.[124] In 1990 the PRI was famously described by Mario Vargas Llosa as the "perfect dictatorship", but by then there had been major challenges to the PRI's hegemony.[125][126][127]
Salinas embarked on a program of neoliberal reforms that fixed the exchange rate of the peso, controlled inflation, opened Mexico to foreign investment, and began talks with the U.S. and Canada to join their free-trade agreement. In order to do that, the Constitution of 1917 was amended in several important ways. Article 27, which had allowed the government to expropriate natural resources and distribute land, was amended to end agrarian reform and to guarantee private owners' property rights. The anti-clerical articles that muzzled religious institutions, especially the Catholic Church, were amended and Mexico reestablished of diplomatic relations with the Holy See. Signing on to the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) removed Mexico's autonomy over trade policy. The agreement came into effect on 1 January 1994; the same day, the Zapatista Army of National Liberation (EZLN) in Chiapas began armed peasant rebellion against the federal government, which captured a few towns, but brought world attention to the situation in Mexico. The armed conflict was short-lived and has continued as a non-violent opposition movement against neoliberalism and globalization. In 1994, following the assassination of the PRI's presidential candidate Luis Donaldo Colosio, Salinas was succeeded by a victorious substitute PRI candidate Ernesto Zedillo. Salinas left Zedillo's government to deal with the Mexican peso crisis, requiring a $50 billion IMF bailout. Major macroeconomic reforms were started by President Zedillo, and the economy rapidly recovered and growth peaked at almost 7% by the end of 1999.[128]
Contemporary Mexico edit
In 2000, after 71 years, the PRI lost a presidential election to Vicente Fox of the opposition conservative National Action Party (PAN). In the 2006 presidential election, Felipe Calderón from the PAN was declared the winner, with a very narrow margin (0.58%) over leftist politician Andrés Manuel López Obrador then the candidate of the Party of the Democratic Revolution (PRD).[129] López Obrador, however, contested the election and pledged to create an "alternative government".[130]
After twelve years, in 2012, the PRI won the presidency again with the election of Enrique Peña Nieto, the governor of the State of Mexico from 2005 to 2011. However, he won with a plurality of about 38%, and did not have a legislative majority.[131]
After founding the new political party MORENA, Andrés Manuel López Obrador won the 2018 presidential election with over 50% of the vote. His political coalition, led by his left-wing party founded after the 2012 elections, includes parties and politicians from all over the political spectrum. The coalition also won a majority in both the upper and lower congress chambers. AMLO's (one of his many nicknames) success is attributed to the country's other strong political alternatives exhausting their chances as well as the politician adopting a moderate discourse with a focus on conciliation.[132]
Mexico has contended with high crime rates, official corruption, narcotrafficking, and a stagnant economy. Many state-owned industrial enterprises were privatized starting in the 1990s, with neoliberal reforms, but Pemex, the state-owned petroleum company is only slowly being privatized, with exploration licenses being issued.[133] In AMLO's push against government corruption, the ex-CEO of Pemex has been arrested.[134]
Although there were fears of electoral fraud in Mexico's 2018 presidential elections,[135] the results gave a mandate to AMLO.[136] On 1 December 2018, Andrés Manuel López Obrador was sworn in as the new President of Mexico. After winning a landslide victory in the July 2018 presidential elections, he became the first leftwing president for decades.[137] In June 2021 midterm elections, López Obrador's left-leaning Morena's coalition lost seats in the lower house of Congress. However, his ruling coalition maintained a simple majority, but López Obrador failed to secure the two-thirds congressional supermajority. The main opposition was a coalition of Mexico's three traditional parties: the center-right Revolutionary Institutional Party, right-wing National Action Party and leftist Party of the Democratic Revolution.[138]
Geography edit
Geographical characteristics edit
Mexico is located between latitudes 14° and 33°N, and longitudes 86° and 119°W in the southern portion of North America. Almost all of Mexico lies in the North American Plate, with small parts of the Baja California peninsula on the Pacific and Cocos Plates. Geophysically, some geographers include the territory east of the Isthmus of Tehuantepec (around 12% of the total) within Central America.[139] Geopolitically, however, Mexico is entirely considered part of North America, along with Canada and the United States.[140]
Mexico's total area is 1,972,550 km2 (761,606 sq mi), making it the world's 13th largest country by total area. It has coastlines on the Pacific Ocean and Gulf of California, as well as the Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea, the latter two forming part of the Atlantic Ocean.[141] Within these seas are about 6,000 km2 (2,317 sq mi) of islands (including the remote Pacific Guadalupe Island and the Revillagigedo Islands). From its farthest land points, Mexico is a little over 2,000 mi (3,219 km) in length. Mexico has nine distinct regions: Baja California, the Pacific Coastal Lowlands, the Mexican Plateau, the Sierra Madre Oriental, the Sierra Madre Occidental, the Cordillera Neo-Volcánica, the Gulf Coastal Plain, the Southern Highlands, and the Yucatán Peninsula.[142] Although Mexico is large, much of its land mass is incompatible with agriculture due to aridity, soil, or terrain. In 2018, an estimated 54.9% of land is agricultural; 11.8% is arable; 1.4% is in permanent crops; 41.7% is permanent pasture; and 33.3% is forest.[143]
Mexico is crossed from north to south by two mountain ranges known as Sierra Madre Oriental and Sierra Madre Occidental, which are the extension of the Rocky Mountains from northern North America. From east to west at the center, the country is crossed by the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt also known as the Sierra Nevada. A fourth mountain range, the Sierra Madre del Sur, runs from Michoacán to Oaxaca. As such, the majority of the Mexican central and northern territories are located at high altitudes, and the highest elevations are found at the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt: Pico de Orizaba (5,700 m or 18,701 ft), Popocatépetl (5,462 m or 17,920 ft) and Iztaccihuatl (5,286 m or 17,343 ft) and the Nevado de Toluca (4,577 m or 15,016 ft). Three major urban agglomerations are located in the valleys between these four elevations: Toluca, Greater Mexico City and Puebla.[citation needed] An important geologic feature of the Yucatán peninsula is the Chicxulub crater. The scientific consensus is that the Chicxulub impactor was responsible for the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Mexico is subject to a number of natural hazards, including hurricanes on both coasts, tsunamis on the Pacific coast, and volcanism.[144]
Mexico has few rivers and lakes. The Lerma River flows west to form Lake Chapala, the country's largest natural lake. The Santiago River flows from Lake Chapala out of the lake to the Pacific Ocean. The Pánuco River flows to the Gulf of Mexico. Lake Pátzcuaro and Lake Cuitzeo, west of Mexico City, are remnants of vast lakes and marshes that covered much of the southern Mesa Central before European settlement. The central lake system where the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan and surrounding communities thrived before the Spanish conquest have almost entirely been drained. There are few permanent streams in the arid Mesa del Norte, and most of these drain into the interior rather than to the ocean. By far the most important river in that part of the country is the Río Bravo del Norte (called the Rio Grande in the United States), which forms a lengthy part of the international border from Ciudad Juárez to the Gulf Coast, 3,141 km (1,952 mi). The Balsas River provides hydroelectric power. Grijalva river and Usumacinta river system drains most of the humid Chiapas Highlands. The Papaloapan River flows into the Gulf of Mexico south of Veracruz, the Grijalva and Usumacinta further southeast are significant Mexican rivers. Both the Baja California Peninsula and the Yucatán Peninsula are extremely arid with no surface streams.
Climate edit
The climate of Mexico is quite varied due to the country's size and topography. Tropic of Cancer effectively divides the country into temperate and tropical zones. Land north of the Tropic of Cancer experiences cooler temperatures during the winter months. South of the Tropic of Cancer, temperatures are fairly constant year-round and vary solely as a function of elevation. This gives Mexico one of the world's most diverse weather systems. Maritime air masses bring seasonal precipitation from May until August. Many parts of Mexico, particularly the north, have a dry climate with only sporadic rainfall, while parts of the tropical lowlands in the south average more than 2,000 mm (78.7 in) of annual precipitation. For example, many cities in the north like Monterrey, Hermosillo, and Mexicali experience temperatures of 40 °C (104 °F) or more in summer. In the Sonoran Desert temperatures reach 50 °C (122 °F) or more.[145]
Descriptors of regions are by temperature, with the tierra caliente (hot land) being coastal up to 900 meters; tierra templada (temperate land) being from 1,800 meters; tierra fría (cold land) extending to 3,500 meters. Beyond the cold lands are the páramos, alpine pastures, and the tierra helada (frozen land) (4,000-4,200 meters) in central Mexico. Areas south of the Tropic of Cancer with elevations up to 1,000 m (3,281 ft) (the southern parts of both coastal plains as well as the Yucatán Peninsula), have a yearly median temperature between 24 to 28 °C (75.2 to 82.4 °F). Temperatures here remain high throughout the year, with only a 5 °C (9 °F) difference between winter and summer median temperatures. Both Mexican coasts, except for the south coast of the Bay of Campeche and northern Baja California, are also vulnerable to serious hurricanes during the summer and fall. Although low-lying areas north of the Tropic of Cancer are hot and humid during the summer, they generally have lower yearly temperature averages (from 20 to 24 °C or 68.0 to 75.2 °F) because of more moderate conditions during the winter.[145]
Biodiversity edit
Mexico ranks fourth[146] in the world in biodiversity and is one of the 17 megadiverse countries. With over 200,000 different species, Mexico is home of 10–12% of the world's biodiversity.[147] Mexico ranks first in biodiversity in reptiles with 707 known species, second in mammals with 438 species, fourth in amphibians with 290 species, and fourth in flora, with 26,000 different species.[148] Mexico is also considered the second country in the world in ecosystems and fourth in overall species.[149] About 2,500 species are protected by Mexican legislation.[149]
In 2002[update], Mexico had the second fastest rate of deforestation in the world, second only to Brazil.[150] It had a 2019 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 6.82/10, ranking it 63rd globally out of 172 countries.[151] The government has taken another initiative in the late 1990s to broaden the people's knowledge, interest and use of the country's esteemed biodiversity, through the Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad.
In Mexico, 170,000 square kilometers (65,637 sq mi) are considered "Protected Natural Areas". These include 34 biosphere reserves (unaltered ecosystems), 67 national parks, 4 natural monuments (protected in perpetuity for their aesthetic, scientific or historical value), 26 areas of protected flora and fauna, 4 areas for natural resource protection (conservation of soil, hydrological basins and forests) and 17 sanctuaries (zones rich in diverse species).[147] Plants indigenous to Mexico are grown in many parts of the world and integrated into their own national cuisines. Some of Mexico's native culinary ingredients include: maize, tomato, beans, squash, chocolate, vanilla, avocado, guava, chayote, epazote, camote, jícama, nopal, zucchini, tejocote, huitlacoche, sapote, mamey sapote, and a great variety of chiles, such as the habanero and the jalapeño. Most of these names come from the indigenous language of Nahuatl. Tequila, the distilled alcoholic drink made from cultivated agave cacti is a major industry. Because of its high biodiversity Mexico has also been a frequent site of bioprospecting by international research bodies.[152] The first highly successful instance being the discovery in 1947 of the tuber "Barbasco" (Dioscorea composita) which has a high content of diosgenin, revolutionizing the production of synthetic hormones in the 1950s and 1960s and eventually leading to the invention of combined oral contraceptive pills.[153]
Government and politics edit
Government edit
The United Mexican States are a federation whose government is representative, democratic and republican based on a presidential system according to the 1917 Constitution. The constitution establishes three levels of government: the federal Union, the state governments and the municipal governments. According to the constitution, all constituent states of the federation must have a republican form of government composed of three branches: the executive, represented by a governor and an appointed cabinet, the legislative branch constituted by a unicameral congress[154][original research?] and the judiciary, which will include a state Supreme Court of Justice. They also have their own civil and judicial codes.
The federal legislature is the bicameral Congress of the Union, composed of the Senate of the Republic and the Chamber of Deputies. The Congress makes federal law, declares war, imposes taxes, approves the national budget and international treaties, and ratifies diplomatic appointments.[155]
The federal Congress, as well as the state legislatures, are elected by a system of parallel voting that includes plurality and proportional representation.[156] The Chamber of Deputies has 500 deputies. Of these, 300 are elected by plurality vote in single-member districts (the federal electoral districts) and 200 are elected by proportional representation with closed party lists[157] for which the country is divided into five electoral constituencies.[158] The Senate is made up of 128 senators. Of these, 64 senators (two for each state and two for Mexico City) are elected by plurality vote in pairs; 32 senators are the first minority or first-runner up (one for each state and one for Mexico City), and 32 are elected by proportional representation from national closed party lists.[157]
The executive is the President of the United Mexican States, who is the head of state and government, as well as the commander-in-chief of the Mexican military forces. The President also appoints the Cabinet and other officers. The President is responsible for executing and enforcing the law, and has the power to veto bills.[159]
The highest organ of the judicial branch of government is the Supreme Court of Justice, the national supreme court, which has eleven judges appointed by the President and approved by the Senate. The Supreme Court of Justice interprets laws and judges cases of federal competency. Other institutions of the judiciary are the Federal Electoral Tribunal, collegiate, unitary and district tribunals, and the Council of the Federal Judiciary.[160] In theory the judiciary is independent of the executive, but President López Obrador moved to recentralize power in the presidency, undermining the independence of a number of institutions. In the judicial realm lowering the salaries of justices, he refused to allow the independent appointment of the attorney general.[161]
Following the fraudulent 1988 Presidential election in hands of the government's Department of Interior (Gobernación), an independent institute to oversee the electoral agency was created, the Federal Institute of Elections, now the National Electoral Institute. In 2022, the López Obrador administration which has feuded with the agency, proposed sweeping changes to the structure, advocating its membership be chosen by voters. The proposal is controversial and opposed by academics, who argue the positions should be held by experts.[162]
Politics edit
Three parties have historically been the dominant parties in Mexican politics: the Institutional Revolutionary Party (PRI), a catch-all party[163] and member of the Socialist International[164] that was founded in 1929 to unite all the factions of the Mexican Revolution and held an almost hegemonic power in Mexican politics since then; the National Action Party (PAN), a conservative party founded in 1939 and belonging to the Christian Democrat Organization of America;[165] and the Party of the Democratic Revolution (PRD) a left-wing party,[166] founded in 1989 as the successor of the coalition of socialists and liberal parties. PRD emerged after what has now been proven was a stolen election in 1988,[167] and has won numerous state and local elections since then. PAN won its first governorship in 1989, and won the presidency in 2000 and 2006.[168] A new political party, National Regeneration Movement (MORENA), a leftist-populist party, emerged after the 2012 election and dominated the 2018 Mexican general election.[169] Unlike many Latin American countries, the military in Mexico does not participate in politics and is under civilian control,[170] the result of the concerted effort of revolutionary generals who became presidents of Mexico (1920–40) to remove the military from politics.[171]
As Mexico transitioned from one-party rule in 2000, increasingly criminal cartels have attempted to meddle in politics and have an impact on electoral outcomes. Cartels have moved from bribing or otherwise influencing politicians and now attempt to have their preferred candidates elected.[172] A recent publication based on two decades of analysis of data contends that "electoral competition and partisan conflict were key drivers of the outbreak of Mexico's crime wars, the intensification of violence, and the expansion of war and violence to the spheres of local politics and civil society."[173]
Foreign relations edit
The foreign relations of Mexico are directed by the President of Mexico[174] and managed through the Ministry of Foreign Affairs.[175] The principles of the foreign policy are constitutionally recognized in the Article 89, Section 10, which include: respect for international law and legal equality of states, their sovereignty and independence, trend to non-interventionism in the domestic affairs of other countries, peaceful resolution of conflicts, and promotion of collective security through active participation in international organizations.[174] Since the 1930s, the Estrada Doctrine has served as a crucial complement to these principles.[176]
Mexico is founding member of several international organizations, most notably the United Nations,[177] the Organization of American States,[178] the Organization of Ibero-American States,[179] the OPANAL[180] and the CELAC.[181] In 2008, Mexico contributed over 40 million dollars to the United Nations regular budget.[182] In addition, it was the only Latin American member of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development since it joined in 1994 until Chile gained full membership in 2010.[183][184]
Mexico is considered a regional power[185][186] hence its presence in major economic groups such as the G8+5 and the G-20. In addition, since the 1990s Mexico has sought a reform of the United Nations Security Council and its working methods[187] with the support of Canada, Italy, Pakistan and other nine countries, which form a group informally called the Coffee Club.[188]
Military edit
The Mexican military "provides a unique example of a military leadership's transforming itself into a civilian political elite, simultaneously transferring the basis of power from the army to a civilian state."[189] The transformation was brought about by revolutionary generals in the 1920s and 1930s, following the demise of the Federal Army following its complete defeat during the decade-long Mexican Revolution.[190] The Mexican Armed Forces are administered by the Secretariat of National Defense (Secretaria de Defensa Nacional, SEDENA). There are two branches: the Mexican Army (which includes the Mexican Air Force), and the Mexican Navy. The Secretariat of Public Security and Civil Protection has jurisdiction over the National Guard, which was formed in 2019 from the disbanded Federal Police and military police of the Army and Navy. Figures vary on personnel, but as of are approximately 223,000 armed forces personnel (160,000 Army; 8,000 Air Force; 55,000 Navy, including about 20,000 marines); approximately 100,000 National Guard (2021). Government expenditures on the military are a small proportion of GDP 0.7% of GDP (2021 est.), 0.6% of GDP (2020).[191]
The Mexican Armed Forces maintain significant infrastructure, including facilities for design, research, and testing of weapons, vehicles, aircraft, naval vessels, defense systems and electronics; military industry manufacturing centers for building such systems, and advanced naval dockyards that build heavy military vessels and advanced missile technologies. Since the 1990s, when the military escalated its role in the war on drugs, increasing importance has been placed on acquiring airborne surveillance platforms, aircraft, helicopters, digital war-fighting technologies,[192] urban warfare equipment and rapid troop transport.[193] Mexico has the capabilities to manufacture nuclear weapons, but abandoned this possibility with the Treaty of Tlatelolco in 1968 and pledged to only use its nuclear technology for peaceful purposes.[194] Mexico signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.[195]
Historically, Mexico has remained neutral in international conflicts,[196] with the exception of World War II. However, in recent years some political parties have proposed an amendment of the Constitution to allow the Mexican Army, Air Force or Navy to collaborate with the United Nations in peacekeeping missions, or to provide military help to countries that officially ask for it.[197]
Law enforcement and crime edit
The Mexican Federal Police were dissolved in 2019 by a constitutional amendment during the administration of President López Obrador and the Mexican National Guard established, amalgamating units of the Federal Police, Military Police, and Naval Police.[198] As of 2022, the National Guard is an estimated at 110,000. López Obrador has increasingly used military forces for domestic law enforcement, particularly against drug cartels.[199] There have been serious abuses of power have been reported in security operations in the southern part of the country and in indigenous communities and poor urban neighborhoods. The National Human Rights Commission has had little impact in reversing this trend, engaging mostly in documentation but failing to use its powers to issue public condemnations to the officials who ignore its recommendations.[200] Most Mexicans have low confidence in the police or the judicial system, and therefore, few crimes are actually reported by the citizens.[201] There have been public demonstrations of outrage against what is considered a culture of impunity.[202]
Crime and human rights violations in Mexico have been criticized, including enforced disappearances (kidnappings), abuses against migrants, extrajudicial killings, gender-based violence, especially femicide, and attacks on journalists and human rights advocatess.[203] A 2020 report by the BBC gives statistics on crime in Mexico, with 10.7 million households with at least one victim of crime.[204] As of May 2022, 100,000 people are officially listed as missing, most since 2007 when President Calderón attempted to stop the drug cartels.[205] Drug cartels remain a major issue in Mexico, with a proliferation of smaller cartels when larger ones are broken up and increasingly the use of more sophisticated military equipment and tactics.[206][207] President Felipe Calderón (2006–12) made eradicating organized crime a top priority by deploying military personnel to cities where drug cartels operate, a move criticized by the opposition parties and the National Human Rights Commission for escalating the violence.[208] Mexico's drug war, ongoing since 2006, has left over 120,000 dead and perhaps another 37,000 missing.[33] Mexican cartels have recently been identified as using the Chinese-sourced synthetic opiate fentanyl, which has caused many drug overdoses in the U.S.[209] China is identified as being involved more generally in organized crime in Mexico.[210] Mexico's National Geography and Statistics Institute estimated that in 2014, one-fifth of Mexicans were victims of some sort of crime.[211] The mass kidnapping of 43 students in Iguala on 26 September 2014 triggered nationwide protests against the government's weak response to the disappearances and widespread corruption that gives free rein to criminal organizations.[212] More than 100 journalists and media workers have been killed or disappeared since 2000, and most of these crimes remained unsolved, improperly investigated, and with few perpetrators arrested and convicted.[213][214] Since President López Obrador became president in 2018, the number of journalists' murders has increased exponentially.[215][216][217] The U.S. Department of State warns its citizens to exercise increased caution when traveling in Mexico, issuing travel advisories on its website.[218]
Administrative divisions edit
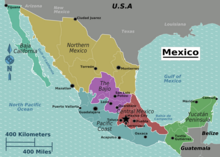
The boundaries and constituent units of Mexico evolved over time from its colonial-era origins. Central America peacefully separated from Mexico after independence in 1821. Yucatán was briefly an independent republic. Texas separated in the Texas Revolution and when it was annexed to the U.S. in 1845, it set the stage for the Mexican–American War and major territorial loss to the U.S. The sale of northern territory known in the U.S. as the Gadsden Purchase was the last loss of Mexican territory. The United Mexican States are a federation of 31 free and sovereign states, which form a union that exercises a degree of jurisdiction over Mexico City.[219] Each state has its own constitution, congress, and a judiciary, and its citizens elect by direct voting a governor for a six-year term, and representatives to their respective unicameral state congresses for three-year terms.[220]
Mexico City is a special political division that belongs to the federation as a whole and not to a particular state.[219] Formerly known as the Federal District, its autonomy was previously limited relative to that of the states.[221] It dropped this designation in 2016 and is in the process of achieving greater political autonomy by becoming a federal entity with its own constitution and congress.[222] The states are divided into municipalities, the smallest administrative political entity in the country, governed by a mayor or municipal president (presidente municipal), elected by its residents by plurality.[223]
Economy edit
As of April 2018, Mexico has the 15th largest nominal GDP (US$1.15 trillion)[224] and the 11th largest by purchasing power parity (US$2.45 trillion). GDP annual average growth was 2.9% in 2016 and 2% in 2017.[224] Agriculture has comprised 4% of the economy over the last two decades, while industry contributes 33% (mostly automotive, oil, and electronics) and services (notably financial services and tourism) contribute 63%.[224] Mexico's GDP in PPP per capita was US$18,714.05. The World Bank reported in 2009 that the country's gross national income in market exchange rates was the second highest in Latin America, after Brazil at US$1,830.392 billion,[225] which led to the highest income per capita in the region at $15,311.[226][227] Mexico is now firmly established as an upper middle-income country. After the slowdown of 2001 the country has recovered and has grown 4.2, 3.0 and 4.8 percent in 2004, 2005 and 2006,[228] even though it is considered to be well below Mexico's potential growth.[229] The International Monetary Fund predicts growth rates of 2.3% and 2.7% for 2018 and 2019, respectively.[224] By 2050, Mexico could potentially become the world's fifth or seventh largest economy.[230][231]
Although multiple international organizations coincide and classify Mexico as an upper middle income country, or a middle class country[232][233] Mexico's National Council for the Evaluation of Social Development Policy (CONEVAL), which is the organization in charge to measure the country's poverty reports that a huge percentage of Mexico's population lives in poverty. According to said council, from 2006 to 2010 (year on which the CONEVAL published its first nationwide report of poverty) the portion of Mexicans who live in poverty rose from 18%–19%[234] to 46% (52 million people).[235] However, rather than Mexico's economy crashing, international economists attribute the huge increase in the percentage of population living below the country's poverty line to the CONEVAL using new standards to define it, as now besides people who lives below the economic welfare line, people who lacks at least one "social need" such as complete education, access to healthcare, access to regular food, housing services and goods, social security etc. were considered to be living in poverty (several countries do collect information regarding the persistence of said vulnerabilities on their population, but Mexico is the only one that classifies people lacking one or more of those needs as living below its national poverty line). Said economists do point out that the percentage of people living in poverty according to Mexico's national poverty line is around 40 times higher than the one reported by the World Bank's international poverty line (with said difference being the biggest in the world) and ponder if it would not be better for countries in the situation of Mexico to adopt internationalized standards to measure poverty so the numbers obtained could be used to make accurate international comparisons.[236] According to the OECD's own poverty line (defined as the percentage of a country's population who earns 60%[237] or less of the national median income) 20% of Mexico's population lives in a situation of poverty.[238]
Among the OECD countries, Mexico has the second-highest degree of economic disparity between the extremely poor and extremely rich, after Chile – although it has been falling over the last decade, being one of few countries in which this is the case.[239] The bottom ten percent in the income hierarchy disposes of 1.36% of the country's resources, whereas the upper ten percent dispose of almost 36%. The OECD also notes that Mexico's budgeted expenses for poverty alleviation and social development is only about a third of the OECD average.[240] This is also reflected by the fact that infant mortality in Mexico is three times higher than the average among OECD nations whereas its literacy levels are in the median range of OECD nations. Nevertheless, according to Goldman Sachs, by 2050 Mexico will have the 5th largest economy in the world.[241] According to a 2008 UN report the average income in a typical urbanized area of Mexico was $26,654, while the average income in rural areas just miles away was only $8,403.[242] Daily minimum wages are set annually being set at $102.68 Mexican pesos (US$5.40) in 2019.[243] All of the indices of social development for the Mexican Indigenous population are considerably lower than the national average, which is motive of concern for the government.[244]
The electronics industry of Mexico has grown enormously within the last decade. Mexico has the sixth largest electronics industry in the world after China, the United States, Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan. Mexico is the second-largest exporter of electronics to the United States where it exported $71.4 billion worth of electronics in 2011.[245] The Mexican electronics industry is dominated by the manufacture and OEM design of televisions, displays, computers, mobile phones, circuit boards, semiconductors, electronic appliances, communications equipment and LCD modules. The Mexican electronics industry grew 20% between 2010 and 2011, up from its constant growth rate of 17% between 2003 and 2009.[245] Currently electronics represent 30% of Mexico's exports.[245]
Mexico produces the most automobiles of any North American nation.[246] The industry produces technologically complex components and engages in some research and development activities.[247] The "Big Three" (General Motors, Ford and Chrysler) have been operating in Mexico since the 1930s, while Volkswagen and Nissan built their plants in the 1960s.[248] In Puebla alone, 70 industrial part-makers cluster around Volkswagen.[247] In the 2010s expansion of the sector was surging. In 2014 alone, more than $10 billion in investment was committed. In September 2016 Kia motors opened a $1 billion factory in Nuevo León,[249] with Audi also opening an assembling plant in Puebla the same year.[250] BMW, Mercedes-Benz and Nissan currently have plants in construction.[251] The domestic car industry is represented by DINA S.A., which has built buses and trucks since 1962,[252] and the new Mastretta company that builds the high-performance Mastretta MXT sports car.[253] In 2006, trade with the United States and Canada accounted for almost 50% of Mexico's exports and 45% of its imports.[12] During the first three quarters of 2010, the United States had a $46.0 billion trade deficit with Mexico.[254] In August 2010 Mexico surpassed France to become the 9th largest holder of US debt.[255] The commercial and financial dependence on the US is a cause for concern.[256]
The remittances from Mexican citizens working in the United States account are significant; after dipping during the after the 2008 Great Recession and again during Covid pandemic in 2021 they are topping other sources of foreign income.[257][258] Remittances are directed to Mexico by direct links from a U.S. government banking program.[259]
Communications edit
The telecommunications industry is mostly dominated by Telmex (Teléfonos de México), previously a government monopoly privatized in 1990. By 2006, Telmex had expanded its operations to Colombia, Peru, Chile, Argentina, Brazil, Uruguay, and the United States. Other players in the domestic industry are Axtel, Maxcom, Alestra, Marcatel, AT&T Mexico.[260] Because of Mexican orography, providing a landline telephone service at remote mountainous areas is expensive, and the penetration of line-phones per capita is low compared to other Latin American countries, at 40 percent; however, 82% of Mexicans over the age of 14 own a mobile phone. Mobile telephony has the advantage of reaching all areas at a lower cost, and the total number of mobile lines is almost two times that of landlines, with an estimation of 63 million lines.[261] The telecommunication industry is regulated by the government through Cofetel (Comisión Federal de Telecomunicaciones).
The Mexican satellite system is domestic and operates 120 earth stations. There is also extensive microwave radio relay network and considerable use of fiber-optic and coaxial cable.[261] Mexican satellites are operated by Satélites Mexicanos (Satmex), a private company, leader in Latin America and servicing both North and South America.[262] It offers broadcast, telephone and telecommunication services to 37 countries in the Americas, from Canada to Argentina. Through business partnerships Satmex provides high-speed connectivity to ISPs and Digital Broadcast Services.[263] Satmex maintains its own satellite fleet with most of the fleet being designed and built in Mexico. Major players in the broadcasting industry are Televisa, the largest Mexican media company in the Spanish-speaking world,[264] TV Azteca and Imagen Televisión.
Energy edit
Energy production in Mexico is managed by the state-owned companies Federal Commission of Electricity and Pemex. Pemex, the public company in charge of exploration, extraction, transportation and marketing of crude oil and natural gas, as well as the refining and distribution of petroleum products and petrochemicals, is one of the largest companies in the world by revenue, making US$86 billion in sales a year.[265][266][267] Mexico is the sixth-largest oil producer in the world, with 3.7 million barrels per day.[268] In 1980 oil exports accounted for 61.6% of total exports; by 2000 it was only 7.3%.[247] The largest hydro plant in Mexico is the 2,400 MW Manuel Moreno Torres Dam in Chicoasén, Chiapas, in the Grijalva River. This is the world's fourth most productive hydroelectric plant.[269]
Mexico is the country with the world's third largest solar potential.[270] The country's gross solar potential is estimated at 5kWh/m2 daily, which corresponds to 50 times national electricity generation.[271] Currently, there is over 1 million square meters of solar thermal panels[272] installed in Mexico, while in 2005, there were 115,000 square meters of solar PV (photo-voltaic). It is expected that in 2012 there will be 1,8 million square meters of installed solar thermal panels.[272] The project named SEGH-CFE 1, located in Puerto Libertad, Sonora, Northwest of Mexico, will have capacity of 46.8 MW from an array of 187,200 solar panels when complete in 2013.[273] All of the electricity will be sold directly to the CFE and absorbed into the utility's transmission system for distribution throughout their existing network. At an installed capacity of 46.8 MWp, when complete in 2013, the project will be the first utility scale project of its kind in Mexico and the largest solar project of any kind in Latin America.
Science and technology edit
The National Autonomous University of Mexico was officially established in 1910,[274] and the university became one of the most important institutes of higher learning in Mexico.[275] UNAM provides world class education in science, medicine, and engineering.[276] Many scientific institutes and new institutes of higher learning, such as National Polytechnic Institute (founded in 1936),[277] were established during the first half of the 20th century. Most of the new research institutes were created within UNAM. Twelve institutes were integrated into UNAM from 1929 to 1973.[278] In 1959, the Mexican Academy of Sciences was created to coordinate scientific efforts between academics.
In 1995, the Mexican chemist Mario J. Molina shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Paul J. Crutzen and F. Sherwood Rowland for their work in atmospheric chemistry, particularly concerning the formation and decomposition of ozone.[279] Molina, an alumnus of UNAM, became the first Mexican citizen to win the Nobel Prize in science.[280]
In recent years, the largest scientific project being developed in Mexico was the construction of the Large Millimeter Telescope (Gran Telescopio Milimétrico, GMT), the world's largest and most sensitive single-aperture telescope in its frequency range.[281] It was designed to observe regions of space obscured by stellar dust. Mexico was ranked 55th in the Global Innovation Index in 2021, up from 56th in 2019.[282][283][284][285]
Tourism edit
As of 2017, Mexico was the 6th most visited country in the world and had the 15th highest income from tourism in the world which is also the highest in Latin America.[286] The vast majority of tourists come to Mexico from the United States and Canada followed by Europe and Asia. A smaller number also come from other Latin American countries.[287] In the 2017 Travel and Tourism Competitiveness Report, Mexico was ranked 22nd in the world, which was 3rd in the Americas.[288]
The coastlines of Mexico harbor many stretches of beaches that are frequented by sunbathers and other visitors. According to national law, the entirety of the coastlines are under federal ownership, that is, all beaches in the country are public. On the Yucatán peninsula, one of the most popular beach destinations is the resort town of Cancún, especially among university students during spring break. Just offshore is the beach island of Isla Mujeres, and to the east is the Isla Holbox. To the south of Cancun is the coastal strip called Riviera Maya which includes the beach town of Playa del Carmen and the ecological parks of Xcaret and Xel-Há. A day trip to the south of Cancún is the historic port of Tulum. In addition to its beaches, the town of Tulum is notable for its cliff-side Mayan ruins. On the Pacific coast is the notable tourist destination of Acapulco. Once the destination for the rich and famous, the beaches have become crowded and the shores are now home to many multi-story hotels and vendors. Acapulco is home to renowned cliff divers: trained divers who leap from the side of a vertical cliff into the surf below. At the southern tip of the Baja California peninsula is the resort town of Cabo San Lucas, a town noted for its beaches and marlin fishing.[289] Further north along the Sea of Cortés is the Bahía de La Concepción, another beach town known for its sports fishing. Closer to the United States border is the weekend draw of San Felipe, Baja California.
Transportation edit
The roadway network in Mexico is extensive and all areas in the country are covered by it. The roadway network in Mexico has an extent of 366,095 km (227,481 mi),[290] of which 116,802 km (72,577 mi) are paved.[291] Of these, 10,474 km (6,508 mi) are multi-lane expressways: 9,544 km (5,930 mi) are four-lane highways and the rest have 6 or more lanes.[291]
Starting in the late nineteenth century, Mexico was one of the first Latin American countries to promote railway development,[201] and the network covers 30,952 km (19,233 mi). The Secretary of Communications and Transport of Mexico proposed a high-speed rail link that will transport its passengers from Mexico City to Guadalajara, Jalisco.[292][293] The train, which will travel at 300 kilometers per hour (190 miles per hour),[294] will allow passengers to travel from Mexico City to Guadalajara in just 2 hours.[294] The whole project was projected to cost 240 billion pesos, or about 25 billion US$[292] and is being paid for jointly by the Mexican government and the local private sector including the wealthiest man in the world, Mexico's billionaire business tycoon Carlos Slim.[295] The government of the state of Yucatán is also funding the construction of a high speed line connecting the cities of Cozumel to Mérida and Chichen Itza and Cancún.[296]
Mexico has 233 airports with paved runways; of these, 35 carry 97% of the passenger traffic.[citation needed] The Mexico City International Airport remains the busiest in Latin America and the 36th busiest in the world[297] transporting 45 million passengers a year.[298]
Demographics edit
Throughout the 19th century, the population of Mexico had barely doubled. This trend continued during the first two decades of the 20th century. The 1921 census reported a loss of about 1 million inhabitants. The Mexican Revolution (c. 1910–1920) greatly impacted population increases. The growth rate increased dramatically between the 1930s and the 1980s, when the country registered growth rates of over 3% (1950–1980). The Mexican population doubled in twenty years, and at that rate it was expected that by 2000 there would be 120 million people living in Mexico. Life expectancy increased from 36 years (in 1895) to 72 years (in the year 2000). According to estimations made by Mexico's National Geography and Statistics Institute, is estimated in 2022 to be 129,150,971[299] as of 2017 Mexico had 123.5 million inhabitants[300] making it the most populous Spanish-speaking country in the world.[301]
Ethnicity and race edit
Mexico's population is highly diverse, but research on Mexican ethnicity has felt the impact of nationalist discourses on identity.[302][303][304] Since the 1930s, the Mexican government has promoted the view that all Mexicans are part of the Mestizo community, within which they are distinguished only by residence in or outside of an indigenous community, degree of fluency in an indigenous language, and degree of adherence to indigenous customs.[305][306] Even then, across the years the government has used different criteria to count Indigenous peoples, with each of them returning considerably different numbers ranging from 6.1%[4] to 23% of the country's population. It is not until very recently that the Mexican government began conducting surveys that consider other ethnic groups that live in the country, such as Afro-Mexicans (who comprised 2% of Mexico's population in 2020)[4] or White Mexicans (47%).[307][308] (These studies assert a view of race based on appearance rather than on self-declared ancestry).[309][310][311] Less numerous groups in Mexico such as Asians and Middle Easterners are also accounted for, with numbers of around 1% each. While Mestizos are a prominent ethnic group in contemporary Mexico, the subjective and ever-changing definition of this category have led to its estimations being imprecise, having been observed that many Mexicans do not identify as Mestizos,[312][313] favoring instead ethnoracial labels such as White or Indigenous due to having more consistent and "static" definitions.[314]
The total percentage of Mexico's indigenous peoples tends to vary depending on the criteria used by the government in its censuses: if the ability to speak an indigenous language is used as the criterion to define a person as indigenous, it is 6.1%,[4][315] if racial self-identification is used, it is 14.9%[316][d] and if people who consider themselves part indigenous are also included, it amounts to 23%.[319] Nonetheless, all the censuses conclude that the majority of Mexico's indigenous population is concentrated in rural areas of the southern and south-eastern Mexican states,[320] with the highest percentages being found in Yucatán (59% of the population), Oaxaca (48%), Quintana Roo (39%), Chiapas (28%), and Campeche (27%).[244][321]
Similarly to Mestizo and indigenous peoples, estimates of the percentage of European-descended Mexicans vary considerably depending on the criteria used: recent nationwide field surveys that account for different phenotypical traits (hair color, skin color etc.) report a percentage between 18%[322]-23%[323] if the criterion is the presence of blond hair, and of 47% if the criterion is skin color, with the later surveys having been conducted by Mexico's government itself.[309][310][311][324][325] While, during the colonial era, most of the European migration into Mexico was Spanish, in the 19th and 20th centuries, a substantial number of non-Spanish Europeans immigrated to the country,[326] with Europeans often being the most numerous ethnic group in colonial Mexican cities.[327][328] Nowadays, Mexico's northern and western regions have the highest percentages of European populations, with the majority of the people not having native admixture or being of predominantly European ancestry.[329]
The Afro-Mexican population (2,576,213 individuals as of 2020[update])[4][330] is an ethnic group made up of descendants of Colonial-era slaves and recent immigrants of sub-Saharan African descent. Mexico had an active slave trade during the colonial period, and some 200,000 Africans were taken there, primarily in the 17th century. The creation of a national Mexican identity, especially after the Mexican Revolution, emphasized Mexico's indigenous and European past; it passively eliminated the African ancestors and contributions. Most of the African-descended population was absorbed into the surrounding Mestizo (mixed European/indigenous) and indigenous populations through unions among the groups. Evidence of this long history of intermarriage with Mestizo and indigenous Mexicans is also expressed in the fact that, in the 2015 inter-census, 64.9% (896,829) of Afro-Mexicans also identified as indigenous. It was also reported that 7.4% of Afro-Mexicans speak an indigenous language.[4][331] The states with the highest self-report of Afro-Mexicans were Guerrero (8.6% of the population), Oaxaca (4.7%) and Baja California Sur (3.3%).[4][332] Afro-Mexican culture is strongest in the communities of the Costa Chica of Oaxaca and Costa Chica of Guerrero.
During the early 20th century, a substantial number of Arabs (mostly Christians)[citation needed] began arriving from the crumbling Ottoman Empire. The largest group were the Lebanese and an estimated 400,000 Mexicans have some Lebanese ancestry.[334]
Smaller ethnic groups in Mexico include South and East Asians, present since the colonial era. During the colonial era, Asians were termed Chino (regardless of ethnicity), and arrived as merchants, artisans and slaves.[335] A study by Juan Esteban Rodríguez, a graduate student at the National Laboratory of Genomics for Biodiversity, indicated that up to one third of people sampled from Guerrero state had significantly more Asian ancestry than most Mexicans, primarily Filipino or Indonesian.[336][337] Modern Asian immigration began in the late 19th century, and at one point in the early 20th century, the Chinese were the second largest immigrant group.[338]
Languages edit
Spanish is the de facto national language spoken by the vast majority of the population, making Mexico the world's most populous Hispanophone country.[339][301] Mexican Spanish refers to the varieties of the language spoken in the country, which differ from one region to another in sound, structure, and vocabulary.[340] In general, Mexican Spanish does not make any phonetic distinction among the letters s and z, as well as c when preceding the vowels e and i, as opposed to Peninsular Spanish. The letters b and v have the same pronunciation as well.[340] Furthermore, the usage of vos, the second person singular pronoun, found in several Latin American varieties, is replaced by tú; whereas vosotros, the second person plural pronoun, fell out of use and was effectively replaced by ustedes.[340] In written form, the Spanish Royal Academy serves as the primary guideline for spelling, except for words of Amerindian origin that retain their original phonology such as cenzontle instead of sinzontle and México not Méjico. Words of foreign origin also maintain their original spelling such as "whisky" and "film", as opposed to güisqui and filme as the Royal Academy suggests.[340] The letter x is distinctly used in Mexican Spanish, where it may be pronounced as
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI (as in oxígeno or taxi); as
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI, particularly in Amerindian words (e.g. mixiote, Xola and uxmal); and as the voiceless velar fricative [x] (such as Texas and Oaxaca).[340]
The federal government officially recognizes sixty-eight linguistic groups and 364 varieties of indigenous languages.[341] It is estimated that around 8.3 million citizens speak these languages,[342] with Nahuatl being the most widely spoken by more than 1.7 million, followed by Yucatec Maya used daily by nearly 850,000 people. Tzeltal and Tzotzil, two other Mayan languages, are spoken by around half a million people each, primarily in the southern state of Chiapas.[342] Mixtec and Zapotec, with an estimated 500,000 native speakers each, are two other prominent language groups.[342] Since its creation in March 2003, the National Indigenous Languages Institute has been in charge of promoting and protecting the use of the country's indigenous languages, through the General Law of Indigenous Peoples' Linguistic Rights, which recognizes them de jure as "national languages" with status equal to that of Spanish.[343] That notwithstanding, in practice, indigenous peoples often face discrimination and do not have full access to public services such as education and healthcare, or to the justice system, as Spanish is the prevailing language.[344]
Aside from indigenous languages, there are several minority languages spoken in Mexico due to international migration such as Low German by the 80,000-strong Mennonite population, primarily settled in the northern states, fueled by the tolerance of the federal government towards this community by allowing them to set their own educational system compatible with their customs and traditions.[345] The Chipilo dialect, a variance of the Venetian language, is spoken in the town of Chipilo, located in the central state of Puebla, by around 2,500 people, mainly descendants of Venetians that migrated to the area in the late 19th century.[346] Furthermore, English is the most commonly taught foreign language in Mexico. It is estimated that nearly 24 million, or around a fifth of the population, study the language through public schools, private institutions or self-access channels.[347] However, a high level of English proficiency is limited to only 5% of the population.[348] Moreover, French is the second most widely taught foreign language, as every year between 200,000 and 250,000 Mexican students enroll in language courses.[349][350][351]
Emigration and immigration edit
In the early 1960s, around 600,000 Mexicans lived abroad, which increased sevenfold by the 1990s to 4.4 million.[352] At the turn of the 21st century, this figure more than doubled to 9.5 million.[352] As of 2017, it is estimated that 12.9 million Mexicans live abroad, primarily in the United States, which concentrates nearly 98% of the expatriate population.[352]
The majority of Mexicans have settled in states such as California, Texas and Illinois, particularly around the metropolitan areas of Los Angeles, Chicago, Houston and Dallas–Fort Worth.[353] As a result of these major migration flows in recent decades, around 36 million U.S. residents, or 11.2% of the country's population, identified as being of full or partial Mexican ancestry.[354]
The remaining 2% of expatriates have settled in Canada (86,000), primarily in the provinces of Ontario and Quebec,[355] followed by Spain (49,000) and Germany (18,000), both European destinations represent almost two-thirds of the Mexican population living in the continent.[352] As for Latin America, it is estimated that 69,000 Mexicans live in the region, Guatemala (18,000) being the top destination for expatriates, followed by Bolivia (10,000) and Panama (5,000).[352]
As of 2017[update], it is estimated that 1.2 million foreigners have settled in Mexico,[356] up from nearly 1 million in 2010.[357] The vast majority of migrants come from the United States (900,000), making Mexico the top destination for U.S. citizens abroad.[358] The second largest group comes from neighboring Guatemala (54,500), followed by Spain (27,600).[356] Other major sources of migration are fellow Latin American countries, which include Colombia (20,600), Argentina (19,200) and Cuba (18,100).[356] Historically, the Lebanese diaspora and the German-born Mennonite migration have left a notorious impact in the country's culture, particularly in its cuisine and traditional music.[359][360] At the turn of the 21st century, several trends have increased the number of foreigners residing in the country such as the 2008–2014 Spanish financial crisis,[361] increasing gang-related violence in the Northern Triangle of Central America,[362] the ongoing political and economic crisis in Venezuela,[363][364] and the automotive industry boom led by Japanese and South Korean investment.[365][366]
Urban areas edit
Template:Largest metropolitan areas of Mexico
Religion edit
Template:Pie chart of the religion in Mexico Although the Constitutions of 1857 and 1917 put limits on the role of the Roman Catholic Church in Mexico, Roman Catholicism remains the country's dominant religious affiliation. The 2020 census by the Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (National Institute of Statistics and Geography) gives Roman Catholicism as the main religion, with 77.7% (97,864,218) of the population, while 11.2% (14,095,307) belong to Protestant/Evangelical Christian denominations—including Other Christians (6,778,435), Evangelicals (2,387,133), Pentecostals (1,179,415), Jehovah's Witnesses (1,530,909), Seventh-day Adventists (791,109), and members of the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints (337,998)—; 8.1% (9,488,671) declared having no religion; .4% (491,814) were unspecified.[4][367]
The 97,864,218[4] Catholics of Mexico constitute in absolute terms the second largest Catholic community in the world, after Brazil's.[368] 47% percent of them attend church services weekly.[369] The feast day of Our Lady of Guadalupe, the patron saint of Mexico, is celebrated on 12 December and is regarded by many Mexicans as the most important religious holiday of their country.[370] The denominations Pentecostal also have an important presence, especially in the cities of the border and in the indigenous communities. As of 2010, Pentecostal churches together have more than 1.3 million adherents, which in net numbers place them as the second Christian creed in Mexico. The situation changes when the different Pentecostal denominations are considered as separate entities. Migratory phenomena have led to the spread of different aspects of Christianity, including branches Protestants, Eastern Catholic Churches and Eastern Orthodox Church.[371]
In certain regions, the profession of a creed other than the Catholic is seen as a threat to community unity. It is argued that the Catholic religion is part of the ethnic identity, and that the Protestants are not willing to participate in the traditional customs and practices (the tequio or community work, participation in the festivities and similar issues). The refusal of the Protestants is because their religious beliefs do not allow them to participate in the cult of images. In extreme cases, tension between Catholics and Protestants has led to the expulsion or even murder of Protestants in several villages. The best known cases are those of San Juan Chamula,[372][373] in Chiapas, and San Nicolás, in Ixmiquilpan,[374] Hidalgo. A similar argument was presented by a committee of anthropologists to request the government of the Republic to expel the Summer Linguistic Institute (SIL), in the year 1979, which was accused of promoting the division of indigenous peoples by translating the Bible into vernacular languages and evangelizing in a Protestant creed that threatened the integrity of popular cultures. The Mexican government paid attention to the call of the anthropologists and canceled the agreement that had held with the SIL.[375]
The presence of Jews in Mexico dates back to 1521, when Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztecs, accompanied by several Conversos.[376] According to the 2020 census, there are 58,876 Jews in Mexico.[4] Islam in Mexico (with 7,982 members) is practiced mostly by Arab Mexicans.[4] In the 2010 census 36,764 Mexicans reported belonging to a spiritualist religion,[4] a category which includes a tiny Buddhist population.
According to Jacobo Grinberg (in texts edited by the National Autonomous University of Mexico), the survival of magic-religious rituals of the old indigenous groups is remarkable, not only in the current indigenous population but also in the mestizo and white population that make up the Mexican rural and urban society. There is often a syncretism between shamanism and Catholic traditions. Another religion of popular syncretism in Mexico (especially in recent years) is the Santería. This is mainly due to the large number of Cubans who settled in the territory after the Cuban Revolution (mainly in states such as Veracruz and Yucatán). Even though Mexico was also a recipient of black slaves from Africa in the 16th century, the apogee of these cults is relatively new.[377] In general, popular religiosity is viewed with bad eyes by institutionally structured religions. One of the most exemplary cases of popular religiosity is the cult of Holy Dead (Santa Muerte). The Catholic hierarchy insists on describing it as a satanic cult. However, most of the people who profess this cult declare themselves to be Catholic believers, and consider that there is no contradiction between the tributes they offer to the Christ Child and the adoration of God. Other examples are the representations of the Passion of Christ and the celebration of Day of the Dead, which take place within the framework of the Catholic Christian imaginary, but under a very particular reinterpretation of its protagonists.[378]
Health edit
In the 1930s, Mexico made a commitment to rural health care, mandating that mostly urban medical students receive training in it and to make them agents of the state to assess marginal areas.[379] Since the early 1990s, Mexico entered a transitional stage in the health of its population and some indicators such as mortality patterns are identical to those found in highly developed countries like Germany or Japan.[380] Mexico's medical infrastructure is highly rated for the most part and is usually excellent in major cities,[381][382] but rural communities still lack equipment for advanced medical procedures, forcing patients in those locations to travel to the closest urban areas to get specialized medical care.[201] Social determinants of health can be used to evaluate the state of health in Mexico.
State-funded institutions such as Mexican Social Security Institute (IMSS) and the Institute for Social Security and Services for State Workers (ISSSTE) play a major role in health and social security. Private health services are also very important and account for 13% of all medical units in the country.[383] Medical training is done mostly at public universities with much specializations done in vocational or internship settings. Some public universities in Mexico, such as the University of Guadalajara, have signed agreements with the U.S. to receive and train American students in medicine. Health care costs in private institutions and prescription drugs in Mexico are on average lower than that of its North American economic partners.[381]
Education edit
In 2004, the literacy rate was at 97%[384] for youth under the age of 14, and 91% for people over 15,[385] placing Mexico at 24th place in the world according to UNESCO.[386]
Nowadays, Mexico's literacy rate is high, at 94.86% in 2018, up from 82.99% in 1980,[387] with the literacy rates of males and females being relatively equal. The National Autonomous University of Mexico ranks 103rd in the QS World University Rankings, making it the best university in Mexico. After it comes the Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education as the best private school in Mexico and 158th worldwide in 2019.[388]
Private business schools also stand out in international rankings. IPADE and EGADE, the business schools of Universidad Panamericana and of Monterrey Institute of Technology and Higher Education respectively, were ranked in the top 10 in a survey conducted by The Wall Street Journal among recruiters outside the United States.[389]
Culture edit
Mexican culture reflects the complexity of the country's history through the blending of indigenous cultures and the culture of Spain during Spain's 300-year colonial rule of Mexico. The Porfirian era (el Porfiriato) (1876–1911), was marked by economic progress and peace. After four decades of civil unrest and war, Mexico saw the development of philosophy and the arts, promoted by President Porfirio Díaz himself. Since that time, as accentuated during the Mexican Revolution, cultural identity has had its foundation in the mestizaje, of which the indigenous (i.e. Amerindian) element is the core. In light of the various ethnicities that formed the Mexican people, José Vasconcelos in La Raza Cósmica (The Cosmic Race) (1925) defined Mexico to be the melting pot of all races (thus extending the definition of the mestizo) not only biologically but culturally as well.[390] Other Mexican intellectuals grappled with the idea of Lo Mexicano, which seeks "to discover the national ethos of Mexican culture."[391] Nobel laureate Octavio Paz explores the notion of a Mexican national character in The Labyrinth of Solitude.
Art edit
Painting is one of the oldest arts in Mexico. Cave painting in Mexican territory is about 7500 years old and has been found in the caves of the Baja California Peninsula. Pre-Columbian Mexico is present in buildings and caves, in Aztec codices, in ceramics, in garments, etc.; examples of this are the Maya mural paintings of Bonampak, or those of Teotihuacán, those of Cacaxtla and those of Monte Albán. Mural painting with Christian religious themes had an important flowering during the 16th century, early colonial era in newly constructed churches and monasteries. Examples can be found in Acolman, Actopan, Huejotzingo, Tecamachalco and Zinacantepec.
As with most art during the early modern era in the West, colonial-era Mexican art was religious during the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries. Starting in the late seventeenth century, and, most prominently in the eighteenth century, secular portraits and images of racial types, so-called casta painting appeared.[392] Important painters of the late colonial period were Juan Correa, Cristóbal de Villalpando and Miguel Cabrera. In early post-independence Mexico, Nineteenth-century painting had a marked romantic influence; landscapes and portraits were the greatest expressions of this era. Hermenegildo Bustos is one of the most appreciated painters of the historiography of Mexican art. Other painters include Santiago Rebull, Félix Parra, Eugenio Landesio, and his noted pupil, the landscape artist José María Velasco.[393]
In the 20th century has achieved world renown with painters such as Diego Rivera, David Alfaro Siqueiros, and José Clemente Orozco, the so-called "Big Three" of Mexican muralism. They were commissioned by the Mexican government to paint large-scale historical murals on the walls of public buildings, which helped shape popular perceptions of the Mexican Revolution and Mexican cultural identity.[394] Frida Kahlo's largely personal portraiture has gained enormous popularity.[395]
Architecture edit
In the 19th century the neoclassical movement arose as a response to the objectives of the republican nation, one of its examples are the Hospicio Cabañas where the strict plastic of the classical orders are represented in their architectural elements, new religious buildings also arise, civilian and military that demonstrate the presence of neoclassicism. Romanticists from a past seen through archeology show images of medieval Europe, Islamic and pre-Columbian Mexico in the form of architectural elements in the construction of international exhibition pavilions looking for an identity typical of the national culture. The art nouveau, and the art deco were styles introduced into the design of the Palacio de Bellas Artes to mark the identity of the Mexican nation with Greek-Roman and pre-Columbian symbols.[citation needed]
The emergence of the new Mexican architecture was born as a formal order of the policies of a nationalist state that sought modernity and the differentiation of other nations. The development of a Mexican modernist architecture was perhaps mostly fully manifested in the mid-1950s construction of the Ciudad Universitaria, Mexico City, the main campus of the National Autonomous University of Mexico. Designed by the most prestigious architects of the era, including Mario Pani, Eugenio Peschard, and Enrique del Moral, the buildings feature murals by artists Diego Rivera, David Alfaro Siqueiros, and José Chávez Morado. It has since been recognized as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.[396]
Juan O'Gorman was one of the first environmental architects in Mexico, developing the "organic" theory, trying to integrate the building with the landscape within the same approaches of Frank Lloyd Wright.[397] In the search for a new architecture that does not resemble the styles of the past, it achieves a joint manifestation with the mural painting and the landscaping. Luis Barragán combined the shape of the space with forms of rural vernacular architecture of Mexico and Mediterranean countries (Spain-Morocco), integrating color that handles light and shade in different tones and opens a look at the international minimalism. He won the 1980 Pritzker Prize, the highest award in architecture.[398]
Cuisine edit
The origin of the current Mexican cuisine was established during the Spanish colonial era, a mixture of the foods of Spain with native indigenous ingredients.[400] Foods indigenous to Mexico include corn, pepper vegetables, calabazas, avocados, sweet potato, turkey, many beans, and other fruits and spices. Similarly, some cooking techniques used today are inherited from pre-Columbian peoples, such as the nixtamalization of corn, the cooking of food in ovens at ground level, grinding in molcajete and metate. With the Spaniards came the pork, beef and chicken meats; peppercorn, sugar, milk and all its derivatives, wheat and rice, citrus fruits and another constellation of ingredients that are part of the daily diet of Mexicans.
From this meeting of millennia old two culinary traditions, were born pozole, mole sauce, barbacoa and tamale is in its current forms, the chocolate, a large range of breads, tacos, and the broad repertoire of Mexican street foods. Beverages such as atole, champurrado, milk chocolate and aguas frescas were born; desserts such as acitrón and the full range of crystallized sweets, rompope, cajeta, jericaya and the wide repertoire of delights created in the convents of nuns in all parts of the country.
In 2005, Mexico presented the candidature of its gastronomy for World Heritage Site of UNESCO, the first time a country had presented its gastronomic tradition for this purpose.[401] The result was negative, because the committee did not place the proper emphasis on the importance of corn in Mexican cuisine.[402] On 16 November 2010 Mexican gastronomy was recognized as Intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO.[403] In addition, Daniela Soto-Innes was named the best female chef in the world by The World's Best 50 Restaurants in April 2019.[404]
Literature edit
Mexican literature has its antecedents in the literature of the indigenous settlements of Mesoamerica. Poetry had a rich cultural tradition in pre-Columbian Mexico, being divided into two broad categories—secular and religious. Aztec poetry was sung, chanted, or spoken, often to the accompaniment of a drum or a harp. While Tenochtitlan was the political capital, Texcoco was the cultural center; the Texcocan language was considered the most melodious and refined. The best well-known pre-Columbian poet is Nezahualcoyotl.[405]
There are historical chronicles of the conquest of Mexico by participants, and, later, by historians. Bernal Díaz del Castillo's True History of the Conquest of the New Spain is still widely read today. Spanish-born poet Bernardo de Balbuena extolled the virtues of Mexico in Grandeza mexicana (Mexican grandeur) (1604). Baroque literature flourished in the 17th century; the most notable writers of this period were Juan Ruiz de Alarcón and Juana Inés de la Cruz. Sor Juana was famous in her own time, called the "Ten Muse."[406]
The late colonial-era novel by José Joaquín Fernández de Lizardi, whose The Mangy Parrot ("El Periquillo Sarniento"), is said to be the first Latin American novel.[406] Nineteenth-century liberal of Nahua origin Ignacio Manuel Altamirano is an important writer of the era, along with Vicente Riva Palacio, the grandson of Mexican hero of independence Vicente Guerrero, who authored a series of historical novels as well as poetry. In the modern era, the novel of the Mexican Revolution by Mariano Azuela (Los de abajo, translated to English as The Underdogs) is noteworthy. Poet and Nobel Laureate Octavio Paz, novelist Carlos Fuentes, Alfonso Reyes, Renato Leduc, essayist Carlos Monsiváis, journalist and public intellectual Elena Poniatowska, and Juan Rulfo (Pedro Páramo), Martín Luis Guzmán, Nellie Campobello, (Cartucho).
Cinema edit
Mexican films from the Golden Age in the 1940s and 1950s are the greatest examples of Latin American cinema, with a huge industry comparable to the Hollywood of those years. Mexican films were exported and exhibited in all of Latin America and Europe. María Candelaria (1943) by Emilio Fernández, was one of the first films awarded a Palme d'Or at the Cannes Film Festival in 1946, the first time the event was held after World War II. The famous Spanish-born director Luis Buñuel realized in Mexico between 1947 and 1965 some of his masterpieces like Los Olvidados (1949) and Viridiana (1961). Famous actors and actresses from this period include María Félix, Pedro Infante, Dolores del Río, Jorge Negrete and the comedian Cantinflas.
More recently, films such as Como agua para chocolate (1992), Sex, Shame, and Tears (1999), Y tu mamá también (2001), and The Crime of Father Amaro (2002) have been successful in creating universal stories about contemporary subjects, and were internationally recognized. Mexican directors Alejandro González Iñárritu (Babel, Birdman, The Revenant, Bardo, False Chronicle of a Handful of Truths), Alfonso Cuarón (A Little Princess, Harry Potter and the Prisoner of Azkaban, Gravity, Roma), Guillermo del Toro (Pan's Labyrinth, Crimson Peak, The Shape of Water, Nightmare Alley), screenwriter Guillermo Arriaga and photographer Emmanuel Lubezki are some of the most known present-day film makers.
Music and dance edit
Mexico has a long tradition of music from the prehispanic era to the present. Much of the music from the colonial era was composed for religious purposes.[407][408]
Although the traditions of European opera and especially Italian opera had initially dominated the Mexican music conservatories and strongly influenced native opera composers (in both style and subject matter), elements of Mexican nationalism had already appeared by the latter part of the 19th century with operas such as Aniceto Ortega del Villar's 1871 Guatimotzin, a romanticized account of the defense of Mexico by its last Aztec ruler, Cuauhtémoc. The most well-known Mexican composer of the twentieth century is Carlos Chávez (1899–1978), who composed six symphonies with indigenous themes, and rejuvenated Mexican music, founding the Orquesta Sinfónica Nacional.[409]
Traditional Mexican music includes mariachi, banda, norteño, ranchera, and corridos. Corridos were particularly popular during the Mexican Revolution (1910–20) and in the present era include narcocorridos. The embrace of rock and roll by young Mexicans in the 1960s and 1970s brought Mexico into the transnational, counterculture movement of the era. In Mexico, the native rock culture merged into the larger countercultural and political movement of the late 1960s, culminating in the 1968 protests and redirected into counterculture rebellion, La Onda (the wave).[410][411]
On an everyday basis most Mexicans listen to contemporary music such as pop, rock, and others in both English and Spanish. Folk dance of Mexico along with its music is both deeply regional and traditional. Founded in 1952, the Ballet Folklórico de México performs music and dance of the prehispanic period through the Mexican Revolution in regional attire in the Palacio de Bellas Artes.[412]
Media edit
There was a major reform of the telecommunications industry in 2013, with the creation of new broadcast television channels. There had been a longstanding limitation on the number of networks, with Televisa, with a virtual monopoly; TV Azteca, and Imagen Television. New technology has allowed the entry of foreign satellite and cable companies. Mexico became the first Latin American country to transition from analog to all digital transmissions.[413]
Telenovelas, or soap operas are very traditional in Mexico and are translated to many languages and seen all over the world. Mexico was a pioneer in edutainment, with TV producer Miguel Sabido creating in 1970s "soap operas for social change". The "Sabido method" has been adopted in many other countries subsequently, including India, Peru, Kenya, and China.[414] The Mexican government successfully used a telenovela to promote family planning in the 1970s to curb the country's high birth rate.[415]
Bilingual government radio stations broadcasting in Spanish and indigenous languages were a tool for indigenous education (1958–65) and since 1979 the Instituto Nacional Indigenista has established a national network of bilingual radio stations.[416]
Sports edit
Organized sport in Mexico largely dates from the late nineteenth century, with only bullfighting having a long history dating to the early colonial era. Once the political turmoil of the early republic was replaced by the stability of the Porfiriato did organized sport become public diversions, with structured and ordered play governed by rules and authorities. Baseball was introduced from the United States and also via Cuba in the 1880s and organized teams were created. After the Mexican Revolution, the government sponsored sports to counter the international image of political turmoil and violence.[417]
The bid to host the 1968 Summer Olympics was to burnish Mexico's stature internationally, with is being the first Latin American country to host the games. The government spent abundantly on sporting facilities and other infrastructure to make the games a success, but those expenditures helped fuel public discontent with the government's lack of spending on social programs.[417] Mexico City hosted the XIX Olympic Games in 1968, making it the first Latin American city to do so.[418] The country has also hosted the FIFA World Cup twice, in 1970 and 1986.[419] Mexico's most popular sport is association football.
The Mexican professional baseball league is named the Liga Mexicana de Beisbol. While usually not as strong as the United States, the Caribbean countries and Japan, Mexico has nonetheless achieved several international baseball titles.[420][421]
Other sporting activities include Bullfighting, boxing, and Lucha Libre (freestyle professional wrestling). Bullfighting (Spanish: corrida de toros) came to Mexico 500 years ago with the arrival of the Spanish. Despite efforts by animal rights activists to outlaw it, bullfighting remains a popular sport in the country, and almost all large cities have bullrings. Plaza México in Mexico City, which seats 45,000 people, is the largest bullring in the world.[422] Freestyle professional wrestling is a major crowd draw with national promotions such as AAA, CMLL and others.[423]
Mexico is an international power in professional boxing.[423] Thirteen Olympic boxing medals have been won by Mexico.[424]
See also edit
- [[Archivo:
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:Iconos|20px|Ver el portal sobre Mexico]] Portal:Mexico. Contenido relacionado con Mexico.
Notes edit
- ^ or Spanish: Méjico, both pronounced
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI ⓘ; Template:Lang-nah, Template:Lang-yua
- ^ Usually, in Spanish, the name of the county is spelled México; however, in Peninsular (European) Spanish, the variant Méjico is used alongside the usual version. According to the Diccionario panhispánico de dudas by the Royal Spanish Academy and Association of Academies of the Spanish Language, the version with J is also correct; however, the spelling with X is recommended, as it is the one used in Mexico.[10]
- ^ Spanish: Estados Unidos Mexicanos,
- REDIRECCIÓN Plantilla:AFI ⓘ, (Template:Lit: United Mexican States), abbreviation: EUM; Nahuatl: Mēxihcatl Tlacetilīlli Tlahtohcāyōtl
- ^ Defined as persons who live in a household where an indigenous language is spoken by one of the adult family members or people who self-identified as indigenous ("Criteria del hogar: De esta manera, se establece, que los hogares indígenas son aquellos en donde el jefe y/o el cónyuge y/o padre o madre del jefe y/o suegro o suegra del jefe hablan una lengua indígena y también aquellos que declararon pertenecer a un grupo indígena."[317]) AND persons who speak an indigenous language but who do not live in such a household ("Por lo antes mencionado, la Comisión Nacional Para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas de México (CDI) considera población indígena (PI) a todas las personas que forman parte de un hogar indígena, donde el jefe(a) del hogar, su cónyuge y/o alguno de los ascendientes (madre o padre, madrastra o padrastro, abuelo(a), bisabuelo(a), tatarabuelo(a), suegro(a)) declaro ser hablante de lengua indígena. Además, también incluye a personas que declararon hablar alguna lengua indígena y que no forman parte de estos hogares."[318])
References edit
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 18. November 2022.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), abgerufen am 11. Oktober 2020.
- ^ Template:Cite CIA World Factbook
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". INEGI, abgerufen am 26. Januar 2021.
- ^ a b c d Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 27. November 2022.
- ^ Inequality - Income inequality - OECD Data. OECD. Retrieved 12 August 2021.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". United Nations Development Programme, 15. Dezember 2020, abgerufen am 15. Dezember 2020 (english).
- ^ INALI: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 13. März 2003, abgerufen am 7. November 2010.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Inali.gob.mx, abgerufen am 18. Juli 2014.
- ^ "México" in Diccionario panhispánico de dudas by Royal Spanish Academy and Association of Academies of the Spanish Language, Madrid: Santillana. 2005. ISBN 978-8-429-40623-8.
- ^ Merriam-Webster's Geographical Dictionary, 3rd ed., Springfield, Massachusetts, United States, Merriam-Webster; p. 733
- ^ a b Mexico. The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 13. Juli 2019.
- ^ Brading, D.A., The First America: The Spanish Monarchy, Creole Patriots, and the Liberal State. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1991. ISBN 052139130X
- ^ Ricard, Robert, The Spiritual Conquest of Mexico, Lesley Byrd Simpson, trans. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press 1966
- ^ Fischer, David Hackett (1996). The Great Wave: Price Revolutions and the Rhythm of History. Oxford University Press. ISBN 978-0-19-505377-7.
- ^ Greenberg, Amy S. (2013). A wicked war : Polk, Clay, Lincoln, and the 1846 U.S. invasion of Mexico. New York. ISBN 978-0-307-47599-2. OCLC 818318029.
- ^ Garner, Paul. Porfirio Díaz. Routledge 2001.
- ^ Jones, Halbert. The War has brought Peace to Mexico: World War II and the Consolidation of the Post-Revolutionary State. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press 2014.
- ^ Sarah Pruitt: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 20. Mai 2022 (english).
- ^ Paweł Bożyk (2006). "Newly Industrialized Countries". Globalization and the Transformation of Foreign Economic Policy. Ashgate Publishing. p. 164. ISBN 978-0-7546-4638-9.
- ^ James Scott, Matthias vom Hau, David Hulme: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] The University of Manchester, archiviert vom Original am 2017-05-25; abgerufen am 11. April 2012.
- ^ Nolte, Detlef (October 2010). "How to compare regional powers: analytical concepts and research topics". Review of International Studies. 36 (4): 881–901. doi:10.1017/S026021051000135X. JSTOR 40961959. S2CID 13809794. ProQuest 873500719.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2007-04-24; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] ipsnews.net, 5. Juni 2007, archiviert vom Original am 2008-08-16; abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ Mauro F. Guillén (2003). "Multinationals, Ideology, and Organized Labor". The Limits of Convergence. Princeton University Press. p. 126 (table 5.1). ISBN 978-0-691-11633-4.
- ^ David Waugh (2000). "Manufacturing industries (chapter 19), World development (chapter 22)". Geography, An Integrated Approach (3rd ed.). Nelson Thornes. pp. 563, 576–579, 633, and 640. ISBN 978-0-17-444706-1.
- ^ N. Gregory Mankiw (2007). Principles of Economics (4th ed.). Mason, Ohio: Thomson/South-Western. ISBN 978-0-324-22472-6.
- ^ [1] UNESCO World Heritage sites, accessed 9 May 2022
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Archiviert vom Original am 2019-09-07; abgerufen am 13. Juli 2019.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CNN Expansión, 28. August 2018, abgerufen am 8. Januar 2019.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Institute for Economics & Peace, Juni 2019, archiviert vom Original am 2019-08-27; abgerufen am 4. Juni 2020.
- ^ a b Brianna Lee; Danielle Renwick; Rocio Cara Labrador (24 January 2019). "Mexico's Drug War". Council on Foreign Relations. Retrieved 19 July 2019.
- ^ William Bright (2004). Native American Placenames of the United States. University of Oklahoma Press. p. 281. ISBN 978-0-8061-3598-4.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] ierd.prd.org.mx, archiviert vom Original am 2008-11-01; abgerufen am 4. November 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". www.tlahui.com, abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Cervantesvirtual.com, 29. November 2010, archiviert vom Original am 2013-08-23; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ Werner 2001, pp. 386–.
- ^ Susan Toby Evans; David L. Webster (2013). Archaeology of Ancient Mexico and Central America: An Encyclopedia. Routledge. p. 54. ISBN 978-1-136-80186-0.
- ^ Colin M. MacLachlan (13 April 2015). Imperialism and the Origins of Mexican Culture. Harvard University Press. p. 39. ISBN 978-0-674-28643-6.
- ^ Carmack, Robert M.; Gasco, Janine L.; Gossen, Gary H. (2016). The Legacy of Mesoamerica: History and Culture of a Native American Civilization. Routledge. ISBN 978-1-317-34678-4.[page needed]
- ^ Diehl, Richard A. (2004). The Olmecs: America's First Civilization. Thames & Hudson. pp. 9–25. ISBN 978-0-500-02119-4.
- ^ Restall, Matthew, "A History of the New Philology and the New Philology in History", Latin American Research Review - Volume 38, Number 1, 2003, pp.113–134
- ^ Sampson, Geoffrey (1985). Writing Systems: A Linguistic Introduction. Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0-8047-1756-4.[page needed]
- ^ Cowgill, George L. (21 October 1997). "State and Society at Teotihuacan, Mexico". Annual Review of Anthropology. 26 (1): 129–161. doi:10.1146/annurev.anthro.26.1.129. OCLC 202300854. S2CID 53663189.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 12. Januar 2017, abgerufen am 14. Juli 2019.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 31. Mai 2014, abgerufen am 13. Juli 2019.
- ^ León Portilla, Miguel (10 May 2009). "Los aztecas, disquisiciones sobre un gentilico". Estudios de Cultura Náhuatl. 31 (31).
- ^ Berdan, et al. (1996), Aztec Imperial Strategies. Dumbarton Oaks, Washington, DC[page needed]
- ^ Coe, Michael D.; Rex Koontz (2002). Mexico: from the Olmecs to the Aztecs (5th edition, revised and enlarged ed.). London and New York: Thames & Hudson. ISBN 978-0-500-28346-2. OCLC 50131575.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Natural History, abgerufen am 16. Dezember 2011.
- ^ Weaver, Muriel Porter (1993). The Aztecs, Maya, and Their Predecessors: Archaeology of Mesoamerica (3rd ed.). San Diego, CA: Academic Press. ISBN 978-0-12-739065-9. OCLC 25832740.
- ^ Florescano, Enrique. "The creation of the Museo Nacional de Antropología and its scientific, educational, and political purposes." In Nationalism: Critical Concepts in Political Science, Vol. IV p. 1257. John Hutchinson and Anthony D. Smith, eds. London and New York: Routledge 2000.
- ^ Octavio Paz, Posdata, Mexico: Siglo Veintiuno 1969, quoted in Florescano, "The creation of the Museo Nacional de Antropología", p. 1258, footnote 9.
- ^ Keen, Benjamin. The Aztec Image in Western Thought. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press 1971. ISBN 9780813515724
- ^ Townsend, Camilla (2006). Malintzin's Choices: An Indian Woman in the Conquest of Mexico. UNM Press. ISBN 978-0-8263-3406-0.[page needed]
- ^ Cortés, Hernán. Five Letters to the Emperor. Trans. J. Bayard Morris. New York: W.W. Norton 1969
- ^ Díaz del Castillo, Bernal. True History of the Conquest of Mexico. various editions. Abridge version translated by J.M. Cohen, The Conquest of New Spain. London: Penguin Books 1963.
- ^ Fuentes, Patricia de. The Conquistadors: First-Person accounts of the Conquest of Mexico. Norman: Norman: University of Oklahoma Press 1993.
- ^ Alva Ixtlilxochitl, Fernando de. Ally of Cortés: Account 13 of the Coming of the Spaniards and the Beginning of Evangelical Law. Trans. Douglass K. Ballentine. El Paso: Texas Western Press 1969.
- ^ Altman, Ida; Cline, S. L.; Pescador, Juan Javier (2003). "Narratives of the Conquest". The Early History of Greater Mexico. Prentice Hall. pp. 73–96. ISBN 978-0-13-091543-6.
- ^ León-Portilla, Miguel. The Broken Spears: The Aztec Accounts of the Conquest of Mexico. Boston: Beacon Press 1992.
- ^ Lockhart, James. We People Here: Nahuatl Accounts of the Conquest of Mexico. Berkeley: University of California Press 1993.
- ^ Lockhart, James and Stuart B. Schwartz. Early Latin America. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1983, 59
- ^ Chuchiak, John F. IV, "Inquisition" in Encyclopedia of Mexico. Chicago: Fitzroy Dearborn 1997, pp. 704–708
- ^ Salvucci, Linda. "Adams-Onís Treaty (1819)". Encyclopedia of Latin American History and Culture, vol. 1, pp. 11–12.
- ^ Francis P. Sempa: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 7. Februar 2017: „Mexico City, the authors [Peter Gordon, Juan Jose Morales] note, was the 'first world city,' the precursor to London, New York, and Hong Kong, where 'Asia, Europe, and the Americas all met, and where people intermingled and exchanged everything from genes to textiles'.“
- ^ Robert McCaa: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 8. Dezember 1997, abgerufen am 13. Juli 2019.
- ^ Sluyter, Andrew (2012). Black Ranching Frontiers: African Cattle Herders of the Atlantic World, 1500–1900. Yale University Press. p. 240. ISBN 9780300179927. Retrieved 8 October 2016.
- ^ Russell, James W. (2009). Class and Race Formation in North America. University of Toronto Press. p. 26. ISBN 9780802096784. Retrieved 13 December 2016.
- ^ Rubén Carrillo: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Asiadémica, abgerufen am 13. Dezember 2016.
- ^ The Penguin Atlas of World Population History, pp. 291–92.
- ^ Victoria Lerner: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] (deutsch: Considerations on the population of New Spain (1793–1810))Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". El Colegio de México, archiviert vom Original am 2018-11-13; abgerufen am 4. Juni 2020 (spanish).
- ^ Cline, Sarah (1 August 2015). "Guadalupe and the Castas". Mexican Studies/Estudios Mexicanos. 31 (2): 218–247. doi:10.1525/mex.2015.31.2.218. S2CID 7995543.
- ^ a b Cope, R. Douglas. The Limits of Racial Domination: Plebeian Society in Colonial Mexico City, 1660–1720. Madison, Wis.: U of Wisconsin, 1994.
- ^ Vinson III, Ben (2017). Before Mestizaje: The Frontiers of Race and Caste in Colonial Mexico. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1-107-02643-8.[page needed]
- ^ Sierra Silva, Pablo Miguel. Urban Slavery in Colonial Mexico: Puebla de los Angeles 1531-1706. New York: Cambridge University Press 2018.
- ^ Deans-Smith, Susan. "Bourbon Reforms" in Encyclopedia of Mexico. p. 156
- ^ "God intervened through Our Lady of Guadalupe to evangelize the Americas, explains Guadalupe expert", Catholic News Agency, 11 August 2009, retrieved 14 July 2019
- ^ a b "Everything You Need To Know About La Virgen De Guadalupe", Huff Post Latino Voices, 12 December 2013, retrieved 14 July 2019
- ^ Ortiz-Ramirez, Eduardo A. The Virgin of Guadalupe and Mexican Nationalism: Expressions of Criollo Patriotism in Colonial Images of the Virgin of Guadalupe. p. 6. ISBN 9780549596509. Retrieved 9 February 2017.[permanent dead link]
- ^ John P. Schmal: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 17. Juli 2003, archiviert vom Original am 2016-03-14; abgerufen am 14. Juli 2019.
- ^ Charlotte M. Gradie (2000). "The Tepehuan Revolt of 1616: Militarism, Evangelism, and Colonialism in Seventeenth-Century Nueva Vizcaya". The Americas. Salt Lake City: University of Utah Press. 58 (2): 302–303. doi:10.1353/tam.2001.0109. S2CID 144896113.
- ^ Wasserstrom, Robert (1980). "Ethnic Violence and Indigenous Protest: The Tzeltal (Maya) Rebellion of 1712". Journal of Latin American Studies. 12: 1–19. doi:10.1017/S0022216X00017533. S2CID 145718069.
- ^ Taylor, William B. (1 June 1979). Drinking, Homicide, and Rebellion in Colonial Mexican Villages (1st ed.). Stanford: Stanford University Press. ISBN 978-0804711128.
- ^ Benjamin White: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 31. Januar 2017, abgerufen am 14. Juli 2019.
- ^ Sandra Knispel: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 13. Dezember 2017, abgerufen am 14. Juli 2019.
- ^ Altman, et al. The Early History of Greater Mexico, 342–43
- ^ "Grito de Dolores". Encyclopaedia Britannica. Retrieved 12 September 2018.
- ^ Van Young, Eric, Stormy Passage: Mexico from Colony to Republic, 1750-1850. (2022), 127.
- ^ Van Young, Stormy Passage, 179–226
- ^ Benson, Nettie Lee. "The Plan of Casa Mata." Hispanic American Historical Review 25 (February 1945): 45–56.
- ^ Hale, Charles A. Mexican Liberalism in the Age of Mora. New Haven: Yale University Press 1968. p. 224
- ^ "Ways of ending slavery". Encyclopædia Britannica.
- ^ Costeloe, Michael P. "Pastry War" in Encyclopedia of Latin American History and Culture, vol. 4, p. 318.
- ^ Van Young, Stormy Passage, "The Age of Santa Anna", 227–270
- ^ Weber, David J., The Mexican Frontier, 1821–1846: The American Southwest under Mexico, University of New Mexico Press, 1982
- ^ Angel Miranda Basurto (2002). La Evolucíon de Mėxico [The Evolution of Mexico] (in Spanish) (6th ed.). Mexico City: Editorial Porrúa. p. 358. ISBN 970-07-3678-4.
- ^ Britton, John A. "Liberalism" in Encyclopedia of Mexico739
- ^ Hamnett, Brian. "Benito Juárez" in Encyclopedia of Mexico, pp. 719–20
- ^ Britton, "Liberalism" p. 740.
- ^ Sullivan, Paul. "Sebastián Lerdo de Tejada" in Encyclopedia of Mexico. pp. 736–38
- ^ Adela M. Olvera: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". (deutsch: The Porfiriato in Mexico)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 2. Februar 2018, abgerufen am 18. Juli 2019 (spanish).
- ^ Hart, John Mason. Empire and Revolution: The Americans in Mexico since the Civil War. Berkeley: University of California Press Du 2002
- ^ Buchenau, Jürgen. "Científicos". Encyclopedia of Mexico, pp. 260–265
- ^ Schmidt, Arthur, "José Ives Limantour" in Encyclopedia of Mexico, pp. 746–49.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 7. Februar 2017 (english).
- ^ Brenner, Anita (1 January 1984). The Wind that Swept Mexico: The History of the Mexican Revolution of 1910–1942 (New ed.). University of Texas Press. ISBN 978-0292790247.
- ^ Benjamin, Thomas. La Revolución: Mexico's Great Revolution as Memory, Myth, and History. Austin: University of Texas Press 2000
- ^ a b c Matute, Alvaro. "Mexican Revolution: May 1917 – December 1920" in Encyclopedia of Mexico, 862–864.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Public Broadcasting Service, 20. November 1910, abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ Robert McCaa: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". University of Minnesota Population Center, abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ Katz, Friedrich. The Secret War in Mexico. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 18. Juli 2019.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 20. Januar 2009, abgerufen am 18. Juli 2019.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 2. März 2017, abgerufen am 18. Juli 2019.
- ^ Rafael Hernández Ángeles: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] (deutsch: 85th anniversary of the founding of the National Revolutionary Party (PRN))Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Archiviert vom Original am 2019-07-19; abgerufen am 18. Juli 2019 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Emayzine, archiviert vom Original am 2007-04-03; abgerufen am 30. September 2007.
- ^ Elena Poniatowska (1975). Massacre in Mexico. Viking, New York. ISBN 978-0-8262-0817-0.
- ^ Kennedy, Duncan (19 July 2008). "Mexico's long forgotten dirty war". BBC News. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ^ Krauze, Enrique (January–February 2006). "Furthering Democracy in Mexico". Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 10 January 2006. Retrieved 7 October 2007.
{{cite magazine}}: Cite magazine requires|magazine=(help) - ^ Schedler, Andreas (2006). Electoral Authoritarianism: The Dynamics of Unfree Competition. L. Rienner Publishers. ISBN 978-1-58826-440-4.
- ^ Crandall, R.; Paz and Roett (2004). "Mexico's Domestic Economy: Policy Options and Choices". Mexico's Democracy at Work. Lynne Reinner Publishers. p. 160. ISBN 978-0-8018-5655-6.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Photius Coutsoukis, abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ Luis Gomez Romero: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 5. Oktober 2018.
- ^ "Vargas Llosa: "México es la dictadura perfecta"". El País. 1 September 1990.
- ^ Reding, Andrew (1991). "Mexico: The Crumbling of the "Perfect Dictatorship"". World Policy Journal. 8 (2): 255–284. JSTOR 40209208.
- ^ Gerardo Cruz Vasconcelos: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2006-07-03; abgerufen am 17. Februar 2007 (spanish).
- ^ Valles Ruiz, Rosa María (June 2016). "Elecciones presidenciales 2006 en México. La perspectiva de la prensa escrita" [2006 presidential Elections in Mexico. The Perspective of the Press]. Revista mexicana de opinión pública (in Spanish) (20): 31–51.
- ^ Reséndiz, Francisco (2006). "Rinde AMLO protesta como "presidente legítimo"". El Universal (in Spanish). Archived from the original on 18 January 2012. Retrieved 1 October 2007.
- ^ "Enrique Pena Nieto wins Mexican presidential election". The Telegraph. 2 July 2012. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 25 August 2015.
- ^ Sieff, Kevin. "López Obrador, winner of Mexican election, given broad mandate". Washington Post.
- ^ Sharma, Gaurav (10 May 2018). "Mexico's Oil And Gas Industry Privatization Efforts Nearing Critical Phase". Forbes. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ Barrera Diaz, Cyntia; Villamil, Justin; Still, Amy (14 February 2020). "Pemex Ex-CEO Arrest Puts AMLO in Delicate Situation". Rigzone. Bloomberg. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ "Mexico's presidential front runner on high alert for election fraud ahead of Sunday's vote". South China Morning Post. Associated Press. 30 June 2018. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 17. Juli 2018, abgerufen am 12. April 2021.
- ^ "Mexico's López Obrador sworn in as first leftist president in decades". BBC News. 2 December 2018.
- ^ Karol Suarez, Rafael Romo and Joshua Berlinger. "Mexico's President loses grip on power in midterm elections marred by violence". CNN.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Grec.cat, archiviert vom Original am 2016-05-15; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ Parsons, Alan; Jonathan Schaffer (May 2004). Geopolitics of oil and natural gas. Economic Perspectives. U.S. Department of State.
- ^ Vargas, Jorge A. (2011). Mexico and the Law of the Sea: Contributions and Compromises. p. 405. ISBN 9789004206205.
- ^ Fact Book Mexico. Accessed 4 May 2022
- ^ [2] [dead link] Mexico Fact Book. accessed 6 May 2022
- ^ [3] [dead link] Mexico Fact Book. accessed 5 May 2022
- ^ a b [4] Encyclopedia Britannica Mexico, accessed 6 May 2022
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 5. Februar 2017 (spanish).
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] SEMARNAT, archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-07; abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] CONEVYT, archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-07; abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ a b Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CONABIO, abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ "Mexico's 'devastating' forest loss". BBC News. 4 March 2002. Retrieved 8 August 2011.
- ^ Grantham, H. S.; Duncan, A.; Evans, T. D.; Jones, K. R.; Beyer, H. L.; Schuster, R.; Walston, J.; Ray, J. C.; Robinson, J. G.; Callow, M.; Clements, T.; Costa, H. M.; DeGemmis, A.; Elsen, P. R.; Ervin, J.; Franco, P.; Goldman, E.; Goetz, S.; Hansen, A.; Hofsvang, E.; Jantz, P.; Jupiter, S.; Kang, A.; Langhammer, P.; Laurance, W. F.; Lieberman, S.; Linkie, M.; Malhi, Y.; Maxwell, S.; Mendez, M.; Mittermeier, R.; Murray, N. J.; Possingham, H.; Radachowsky, J.; Saatchi, S.; Samper, C.; Silverman, J.; Shapiro, A.; Strassburg, B.; Stevens, T.; Stokes, E.; Taylor, R.; Tear, T.; Tizard, R.; Venter, O.; Visconti, P.; Wang, S.; Watson, J. E. M. (8 December 2020). "Anthropogenic modification of forests means only 40% of remaining forests have high ecosystem integrity". Nature Communications. 11 (1): 5978. Bibcode:2020NatCo..11.5978G. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-19493-3. PMC 7723057. PMID 33293507.
- ^ Hayden, Cori. 2003. When Nature Goes Public: The Making and Unmaking of Bioproscpecting in Mexico. Princeton University Press.
- ^ Laveaga, Gabriela Soto (2009). Jungle Laboratories: Mexican Peasants, National Projects, and the Making of the Pill. Duke University Press. ISBN 978-0-8223-9196-8.[page needed]
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 27. Januar 2019 (english).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, archiviert vom Original am 2006-11-13; abgerufen am 3. Oktober 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, 15. August 1990, archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-25; abgerufen am 3. Oktober 2007 (spanish).
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, 15. August 1990, archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-25; abgerufen am 3. Oktober 2007 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, 15. August 1990, archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-25; abgerufen am 3. Oktober 2007 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, archiviert vom Original am 2006-11-13; abgerufen am 3. Oktober 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, archiviert vom Original am 2006-11-13; abgerufen am 3. Oktober 2007.
- ^ [5] "Interamerican Dialogue", Vanda Felbab Brown. Brookings Institution, accessed 19 May 2022
- ^ "Mexico leader proposes electoral reforms" Los Angeles Times accessed 3 May 2022
- ^ Niko Vorobyov, ed. (2019). Dopeworld: Adventures in Drug Lands. Hachette UK. ISBN 9781317755098.
... Mexico spent most of the twentieth century governed by the Institutional Revolutionary Party or PRI, a bigtent, catch-all alliance that included everyone ...
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] 17. Dezember 2008, archiviert vom Original am 2008-12-17; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] ODCA, 14. Juli 2008, archiviert vom Original am 2008-07-14; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2013-01-16; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ Ginger Thompson: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 9. März 2004, abgerufen am 19. Juli 2019.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 14. September 2014, archiviert vom Original am 2019-08-13; abgerufen am 19. Juli 2019.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". (deutsch: What is Morena, and when was it founded?)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 5. Juli 2018, abgerufen am 19. Juli 2019 (spanish).
- ^ Camp, Generals in the Palacio p.6
- ^ Lieuwen, Edwin, Mexican Militarism: The Rise and Fall of the Revolutionary Army, 1910-1940. Westport CT: Greenwood Publishers 1981. ISBN 0313229112
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 24. Januar 2022, abgerufen am 19. Mai 2022.
- ^ Trejo, Guillermo and Sandra Ley. Votes, Drugs, and Violence: The Political Logic of Criminal Wars in Mexico. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 2020, publisher's summary. ISBN 978-1108841740
- ^ a b Political Constitution of the United Mexican States: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Chamber of Deputies, 5. Februar 1917, archiviert vom Original am 2007-08-25; abgerufen am 28. März 2009 (spanish).
- ^ Internal Rules of the Ministry of Foreign Affairs: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Ministry of Foreign Affairs, 10. August 2001, archiviert vom Original am 2008-06-11; abgerufen am 28. März 2009 (spanish).
- ^ Jorge Palacios Treviño: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2009-02-06; abgerufen am 4. April 2009 (spanish).
- ^ UN: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] UN official website, 7. November 1945, archiviert vom Original am 2009-04-17; abgerufen am 6. April 2009.
- ^ Velázquez Flores (2007), p. 145.
- ^ Organization of Ibero-American States: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". OEI official website, abgerufen am 6. April 2009 (spanish).
- ^ OPANAL: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] OPANAL official website, archiviert vom Original am 2009-08-14; abgerufen am 6. April 2009.
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Gobierno Federal, 7. März 2007, archiviert vom Original am 2009-08-23; abgerufen am 6. April 2009 (spanish).
- ^ United Nations: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Global Policy, 2008, abgerufen am 4. April 2009.
- ^ Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". OECD official website, 18. Mai 1994, abgerufen am 6. April 2009.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 12. Januar 2010, abgerufen am 23. April 2010.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Japan, abgerufen am 4. April 2009.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Oxford Analytica, archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-24; abgerufen am 4. April 2009.
- ^ Ministry of Foreign Affairs (2005), p. 215.
- ^ Maggie Farley (22 July 2005). "Mexico, Canada Introduce Third Plan to Expand Security Council". Los Angeles Times. Retrieved 4 April 2009.
- ^ Camp, Roderic Ai. Generals in the Palacio: The Military in Modern Mexico. New York: Oxford University Press 1992, p.6
- ^ Lieuwen, Edwin. Mexican Militarism. Albuquerque: University of New Mexico Press 1968
- ^ [6] [dead link] World Fact Book, Mexico. accessed 4 May 2022
- ^ Loke: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Impreso.milenio.com, archiviert vom Original am 2010-05-14; abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2017-01-25; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Opanal.org, 27. November 1963, archiviert vom Original am 2011-04-30; abgerufen am 9. März 2011.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". United Nations Treaty Collection, 7. Juli 2017.
- ^ Gustavo Iruegas: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 27. April 2007, abgerufen am 4. April 2009 (spanish).
- ^ Ricardo Gómez, Andrea Merlos: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] El Universal, 20. April 2007, archiviert vom Original am 2013-10-15; abgerufen am 4. April 2009 (spanish).
- ^ "A Look At Mexico's New National Guard". NPR. 13 July 2019. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- ^ [7] [dead link] World Fact Book accessed 14 May 2022.
- ^ "Big, expensive and weirdly spineless". The Economist. 14 February 2008. Retrieved 17 July 2013.
- ^ a b c Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Britannica Online Encyclopedia, abgerufen am 6. März 2011.
- ^ "A Woman's Haunting Disappearance Sparks Outrage in Mexico Over Gender Violence" New York Times accessed 17 May 2022.
- ^ "Mexico: Events of 2021". World Report, Mexico 2022. Human Rights Watch.org. Human Rights Watch. 10 December 2021. Retrieved 14 May 2022.
- ^ "Mexico crime and violence in numbers" BBC News, accessed 8 May 2022
- ^ "Mexico disappearances reach record high of 100,000 amid impunity" BBC News accessed 17 May 2022.
- ^ [8] "In Mexico, One Cartel Is Cleared, but Others Storm In" New York Times, accessed 8 May 2022
- ^ [9] "How Mexico's Cartels Have Learned Military Tactics", accessed 8 May 2022
- ^ Olivares Alonso, Emir (5 February 2018), "Gobierno de Calderón mantiene récord en violaciones a derechos" [Government of Calderon has a record of violations of rights], La Jornada (in Spanish), Mexico City, retrieved 11 July 2019
- ^ [10] "Fentanyl deaths Climbing". U.S. Drug Enforcement Agency accessed 8 May 2022
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 23. Februar 2022, abgerufen am 19. Mai 2022.
- ^ Franco, Yanira (1 October 2015). "Uno de cada cinco, víctima de algún delito: Inegi" [One in five, victim of a crime: Inegi]. Milenio (in Spanish). Mexico City. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ Tuckman, Jo (21 November 2014). "Mexicans in biggest protest yet over missing students". The Guardian. Mexico City. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] PEN American Center, archiviert vom Original am 2013-07-23.
- ^ Alcázar, Jesús (17 July 2014). "Más de 100 periodistas asesinados en México desde el año 2000" (in Spanish). El Mundo (Spain). EFE.
- ^ [11] Ninth Journalist Killed this year as Violence against Media Soars. The Guardian, accessed 7 May 2022
- ^ [12] "2 journalists killed in Mexico — the 10th and 11th of the year" Los Angeles Times accessed 11 May 2022
- ^ "Why do journalists in Mexico keep getting killed?" Washington Post accessed 11 May 2022
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". U.S. Department of State — Bureau of Consular Affairs, 17. Dezember 2019, abgerufen am 4. Juni 2020.
- ^ a b Amanda Briney: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Thought.Co., 8. Oktober 2018, abgerufen am 15. Juli 2019.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, archiviert vom Original am 2006-11-13; abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, archiviert vom Original am 2006-11-13; abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 30. Januar 2016, archiviert vom Original am 2017-07-21; abgerufen am 5. Januar 2018.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Congress of the Union of the United Mexican States, archiviert vom Original am 2006-11-13; abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ a b c d Caleb Silver: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 7. Juni 2019, abgerufen am 15. Juli 2019.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2010-11-05; abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2010.
- ^ Andrew Jacobs; Matt Richtel (11 December 2017). "A Nasty, Nafta-Related Surprise: Mexico's Soaring Obesity". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 12 December 2017. Retrieved 12 December 2017.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 27. Dezember 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2007-06-15; abgerufen am 16. Februar 2007 (spanish).
- ^ Hufbauer, G.C.; Schott, J.J. (1 January 2005), "Chapter 1, Overview" (PDF), NAFTA Revisited: Achievements and Challenges, Washington, DC: Institute for International Economics (published October 2005), pp. 1–78, ISBN 978-0-88132-334-4
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] 17. März 2010, archiviert vom Original am 2010-08-19; abgerufen am 12. Juli 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] PwC Economics, archiviert vom Original am 2013-02-22; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ "How much should you earn in Mexico to belong to the middle or upper class?". The Mazatlan Post. 11 April 2019. Retrieved 15 July 2019.
- ^ Smith, Noah (26 August 2019). "Mexico Is Solidly Middle Class (No Matter What Trump Says)". Bloomberg.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". United Nations, S. 118, abgerufen am 4. Juni 2020.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2013-10-21; abgerufen am 31. März 2012.
- ^ Ugo Gentilini, Andy Sumner: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Oxfam, 24. Juli 2012, archiviert vom Original am 2020-05-11; abgerufen am 4. Juni 2020.
- ^ Michael Blastland (31 July 2009). "Just what is poor?". BBC News. Retrieved 27 August 2019. The "economic distance" concept, and a level of income set at 60% of the median household income
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". OECD Publishing, 2019, abgerufen am 4. Juni 2020.
- ^ Income inequality. Society at a Glance 2011: Social Indicators. OECD. 12 April 2011. ISBN 9789264098527. Retrieved 16 March 2013.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". OECD, Januar 2012, S. 35–36, abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2010-03-31; abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ "Sobresale Nuevo León por su alto nivel de vida". El Norte (in Spanish). 2006.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". (deutsch: The increase in the minimum wage starts today)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 1. Januar 2019, abgerufen am 19. Juli 2019 (spanish).
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI), archiviert vom Original am 2013-10-09; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ a b c Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". PR Newswire, 6. Oktober 2011, abgerufen am 23. April 2014.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Upi.com, 11. Dezember 2008, abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ a b c Gereffi, G; Martínez, M (2005). "Mexico's Economic Transformation under NAFTA". In Crandall, R; Paz, G; Roett, R (eds.). Mexico's Democracy at Work: Political and Economic Dynamics. Lynne Reiner Publishers (published 30 September 2004). ISBN 978-1-58826-300-1.
- ^ Hufbauer, G.C.; Schott, J.J . (1 January 2005). "Chapter 6, The Automotive Sector" (PDF). NAFTA Revisited: Achievements and Challenges. Washington, D.C.: Institute for International Economics (published October 2005). pp. 1–78. ISBN 978-0-88132-334-4.
- ^ García, Daniela (7 September 2016). "Inauguran Kia Motors en Pesquería" [Kia Motors launched in Pesquería]. Milenio (in Spanish). Pesquería. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ "Audi inaugura planta automotriz en Puebla" [Audi opens automotive plant in Puebla]. Autoexplora (in Spanish). 30 September 2016. Archived from the original on 27 September 2020. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ "Automaker Kia plans $1 bn assembly plant in Mexico". Mexico News.Net. 28 August 2014. Retrieved 28 August 2014.
- ^ DINA Camiones Company: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2011-05-13; abgerufen am 15. April 2009.
- ^ Jeremy Korzeniewski: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 30. Juli 2008.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2011-05-01; abgerufen am 9. März 2011.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". U.S. Department of the Treasury, abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ Thompson, Adam (20 June 2006). "Mexico, Economics: The US casts a long shadow". Financial Times. Archived from the original on 23 October 2012.
- ^ [13] "Personal Remittances Received, Mexico", World Bank accessed 11 May 2022
- ^ [14] "Latino Remittances from Mexico Soar". NBC News accessed 11 May 2022
- ^ [15] "Most of the $33 Billion in Remittances to Mexico Flow Via U.S. Govt. Banking Program", Judicial Watch, accessed 12 May 2022
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 2019, abgerufen am 15. Juli 2019.
- ^ a b Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CIA Factbook, abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] 15. September 2009, archiviert vom Original am 2009-09-15; abgerufen am 17. Juli 2013.
- ^ Source: Arianespace: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Spaceref.com, 14. Februar 2002, abgerufen am 8. August 2011.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Snellwilcox.com, archiviert vom Original am 2007-12-14; abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ América Economia: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". (Requires subscription) Abgerufen am 16. Februar 2007. [dead link]
- ^ "Fortune Global 500 2010: 64. Pemex". Fortune. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- ^ "FT Non-Public 150 – the full list". Financial Times. 14 December 2006. Archived from the original on 11 December 2022. Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- ^ Energy Information Administration: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2007-02-16; abgerufen am 16. Februar 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Eia.doe.gov, archiviert vom Original am 2006-03-09; abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2010.
- ^ Sener & GTZ 2006
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2008-10-03; abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2010.
- ^ a b SENER 2009b
- ^ Sonora Energy Group Hermosillo
- ^ Coerver, Don M.; Pasztor, Suzanne B.; Buffington, Robert (2004). Mexico: An Encyclopedia of Contemporary Culture and History. ABC-CLIO. p. 161. ISBN 978-1-57607-132-8.
- ^ Summerfield, Devine & Levi (1998), p. 285Template:Full citation needed
- ^ Summerfield, Devine & Levi (1998), p. 286Template:Full citation needed
- ^ Forest & Altbach (2006), p. 882Template:Full citation needed
- ^ Fortes & Lomnitz (1990), p. 18Template:Full citation needed
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Nobel Foundation, abgerufen am 2. Januar 2009.
- ^ Thomson, Elizabeth A.: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 18. Oktober 1995, abgerufen am 2. Januar 2009.
- ^ Carramiñana, Alberto (2007). "Unravelling unidentified γ-ray sources with the large millimeter telescope". The Multi-Messenger Approach to High-Energy Gamma-Ray Sources. pp. 527–530. doi:10.1007/978-1-4020-6118-9_79. ISBN 978-1-4020-6117-2.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". United Nations, abgerufen am 5. März 2022 (english).
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 2. September 2021 (english).
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Abgerufen am 2. September 2021.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 28. Oktober 2013, archiviert vom Original am 2021-09-02; abgerufen am 2. September 2021 (english).
- ^ UNWTO Tourism Highlights. World Tourism Organization (UNWTO). 2017. doi:10.18111/9789284419029. ISBN 978-92-844-1902-9.[page needed]
- ^ SECTUR: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Secretaría de Turismo (SECTUR), 2006, archiviert vom Original am 2008-06-10; abgerufen am 26. Juli 2008 (spanish). pp. 5
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". World Economic Forum, April 2017.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] icabo.com, archiviert vom Original am 2013-05-02; abgerufen am 23. April 2014.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CIA, abgerufen am 20. Dezember 2010.
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Secretaría de Comunicaciones y Transportes, archiviert vom Original am 2007-07-16; abgerufen am 13. Januar 2007.
- ^ a b Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Azcentral.com, 6. Januar 2006, abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2010. [dead link]
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 17. Oktober 2003, archiviert vom Original am 2011-04-30; abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2010.
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Systra, archiviert vom Original am 2011-05-01; abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2010.
- ^ "Slim to invest in Santa Cruz". The America's Intelligence Wire. 21 January 2005. Archived from the original on 18 January 2012.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Articlealley.com, 25. August 2010, abgerufen am 30. Oktober 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] AICM, archiviert vom Original am 2008-05-31; abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Mexico City International Airport, archiviert vom Original am 2018-01-14; abgerufen am 12. Januar 2018.
- ^ [16] [dead link] World Fact Book, Mexico. accessed 5 May 2022
- ^ "México cuenta con 123.5 millones de habitantes" [Mexico has 123.5 million inhabitants]. El Economista (in Spanish). Notimex. 10 July 2017. Retrieved 4 June 2020.
- ^ a b [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Today Translations, archiviert vom Original am 2005-04-17; abgerufen am 1. Oktober 2007.
- ^ Knight, Alan. 1990. "Racism, Revolution and indigenismo: Mexico 1910–1940". Chapter 4 in The Idea of Race in Latin America, 1870–1940. Richard Graham (ed.) pp. 78–85
- ^ Wimmer, Andreas, 2002. Nationalist Exclusion and Ethnic Conflict: Shadows of Modernity, Cambridge University Press page 115
- ^ Hall Steckel, Richard; R. Haines, Michael (2000). A population history of North America. Cambridge University Press. p. 621. ISBN 978-0-521-49666-7.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2013-08-23.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Redalyc.org, 16. März 2005, archiviert vom Original am 2013-10-22; abgerufen am 27. Juni 2013.
- ^ Fuentes-Nieva, Ricardo (6 July 2017). "Ser blanco" [Be white]. El Universal (in Spanish).
- ^ Solís, Arturo (7 August 2018). "Comprobado con datos: en México te va mejor si eres blanco" [Proven with data: in Mexico you do better if you are white]. Forbes México (in Spanish).
- ^ a b "21 de Marzo Día Internacional de la Eliminación de la Discriminación Racial" pag.7, CONAPRED, Mexico, 21 March. Retrieved on 28 April 2017.
- ^ a b "Encuesta Nacional Sobre Discriminación en Mexico", "CONAPRED", Mexico DF, June 2011. Retrieved on 28 April 2017.
- ^ a b "DOCUMENTO INFORMATIVO SOBRE DISCRIMINACIÓN RACIAL EN MÉXICO", CONAPRED, Mexico, 21 March 2011, retrieved on 28 April 2017.
- ^ Schwartz-Marín, Ernesto; Silva-Zolezzi, Irma (2010). ""The Map of the Mexican's Genome": Overlapping national identity, and population genomics". Identity in the Information Society. 3 (3): 489–514. doi:10.1007/s12394-010-0074-7. hdl:10871/33766.
- ^ R. Martínez & C. De La Torre (2008): "Racial Appearance And Income In Contemporary Mexico, pag 9 note 1", Journal of Diversity Management, 2008, Retrieved 1 April 2021.
- ^ Federico Navarrete Linares: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] (deutsch: The miscegenation in Mexico)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Archiviert vom Original am 2017-08-01; abgerufen am 31. Juli 2017 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Inegi.gob.mx, archiviert vom Original am 2012-01-18; abgerufen am 10. Dezember 2011.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas, 2006, archiviert vom Original am 2016-03-04; abgerufen am 22. Dezember 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] (deutsch: What is and how an indigenous home is determined?)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CDI. Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas [CDI. National Commission for the Development of Indigenous Peoples), 23. Februar 2009, archiviert vom Original am 2011-05-01 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] (deutsch: Information system and indicators on the indigenous population of Mexico)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CDI. Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas [CDI. National Commission for the Development of Indigenous Peoples, archiviert vom Original am 2011-05-01 (spanish).
- ^ "Encuesta Intercensal 2015" Archived 22 April 2017 at the Wayback Machine, "INEGI", Mexico, December 2015. Retrieved on 28 April 2017.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] (deutsch: Socio-economic indicators of indigenous peoples)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Comisión Nacional para el Desarrollo de los Pueblos Indígenas, archiviert vom Original am 2004-11-15 (spanish).
- ^ Navarrete Linares, Federico (2008). Los pueblos indígenas de México [Indigenous peoples of Mexico] (in Spanish). México: CDI. ISBN 978-970-753-157-4. Archived from the original on 30 November 2011 – via cdi.gob.mx.
- ^ Villarreal, Andrés (October 2010). "Stratification by Skin Color in Contemporary Mexico". American Sociological Review. American Sociological Association. 75 (5): 652–678. doi:10.1177/0003122410378232. JSTOR 20799484. S2CID 145295212.
- ^ Ortiz-Hernández, Luis; Compeán-Dardón, Sandra; Verde-Flota, Elizabeth; Flores-Martínez, Maricela Nanet (April 2011). "Racism and mental health among university students in Mexico City". Salud Pública de México. 53 (2): 125–133. doi:10.1590/s0036-36342011000200005. PMID 21537803.
- ^ "Encuesta Nacional sobre Discriminación 2017", CNDH, 6 August 2018, Retrieved on 9 August 2018.
- ^ "Visión INEGI 2021 Dr. Julio Santaella Castell", INEGI, 3 July 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018.
- ^ Sherburne Friend Cook; Woodrow Borah (1998). Ensayos sobre historia de la población. México y el Caribe 2. Siglo XXI. p. 223. ISBN 9789682301063. Retrieved 12 September 2017.
- ^ San Miguel, G. (November 2000). "Ser mestizo en la nueva España a fines del siglo XVIII: Acatzingo, 1792" [To be «mestizo» in New Spain at the end of the XVIII th century. Acatzingo, 1792]. Cuadernos de la Facultad de Humanidades y Ciencias Sociales. Universidad Nacional de Jujuy (in Spanish) (13): 325–342.
- ^ Howard F. Cline (1963). THE UNITED STATES AND MEXICO. Harvard University Press. p. 104. ISBN 9780674497061. Retrieved 18 May 2017.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". INEGI, abgerufen am 28. September 2016.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] (deutsch: Main results — Intercensal Survey 2015)Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". INEGI, 2015, archiviert vom Original am 2017-03-13; abgerufen am 4. Juni 2020 (spanish).
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". INEGI, abgerufen am 24. Dezember 2015.
- ^ Ruiz-Linares, Andrés; Adhikari, Kaustubh; Acuña-Alonzo, Victor; Quinto-Sanchez, Mirsha; Jaramillo, Claudia; Arias, William; Fuentes, Macarena; Pizarro, María; Everardo, Paola; de Avila, Francisco; Gómez-Valdés, Jorge; León-Mimila, Paola; Hunemeier, Tábita; Ramallo, Virginia; Silva de Cerqueira, Caio C.; Burley, Mari-Wyn; Konca, Esra; de Oliveira, Marcelo Zagonel; Veronez, Mauricio Roberto; Rubio-Codina, Marta; Attanasio, Orazio; Gibbon, Sahra; Ray, Nicolas; Gallo, Carla; Poletti, Giovanni; Rosique, Javier; Schuler-Faccini, Lavinia; Salzano, Francisco M.; Bortolini, Maria-Cátira; Canizales-Quinteros, Samuel; Rothhammer, Francisco; Bedoya, Gabriel; Balding, David; Gonzalez-José, Rolando (25 September 2014). "Admixture in Latin America: Geographic Structure, Phenotypic Diversity and Self-Perception of Ancestry Based on 7,342 Individuals". PLOS Genetics. 10 (9): e1004572. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004572. PMC 4177621. PMID 25254375.
- ^ Langley, William (7 July 2007). "The biggest enchilada". The Telegraph. Archived from the original on 10 January 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2015.
- ^ Tatiana Seijas (2014). Asian Slaves in Colonial Mexico: From Chinos to Indian. Cambridge University Press. p. 21. ISBN 9781107063129.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 12. April 2018.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-15.
- ^ Chao Romero, Robert (2011). "1. Introduction". The Chinese in Mexico, 1882–1940. University of Arizona Press. p. 1. ISBN 9780816508198. Retrieved 1 October 2016.
- ^ Template:Ethnologue18
- ^ a b c d e Werner 2001, pp. 443, 444, 445.
- ^ INALI [Instituto Nacional de Lenguas Indígenas] (14 January 2008). "Catálogo de las lenguas indígenas nacionales: Variantes lingüísticas de México con sus autodenominaciones y referencias geoestadísticas" (PDF online facsimile). Diario Oficial de la Federación (in Spanish). Mexico City. 652 (9): 22–78 (first section), 1–96 (second section), 1–112 (third section). OCLC 46461036.
- ^ a b c Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". National Institute of Statistics and Geography, 2015, abgerufen am 11. September 2018.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] 2003, archiviert vom Original am 2013-09-21; abgerufen am 3. August 2017 (spanish).
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". National Indigenous Languages Institute, Oktober 2012, S. 7, abgerufen am 11. September 2018 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2007-02-05; abgerufen am 11. September 2018.
- ^ Template:E18
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". British Council, Mai 2015, abgerufen am 11. September 2018.
- ^ Isabel Becerril: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". El Financiero, 27. April 2015, abgerufen am 11. September 2018 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Organisation internationale de la Francophonie, 6. September 2010, S. 132, archiviert vom Original am 2018-11-13; abgerufen am 11. September 2018 (french).
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Ambassade de France à Mexico, 19. März 2013, abgerufen am 11. September 2018 (french).
- ^ Nathalie Simon-Clerc: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". L'Outarde Libérée, 2. November 2016, abgerufen am 11. September 2018 (french).
- ^ a b c d e Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". BBVA Research, 2018, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Migration Policy Institute, 17. März 2016, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] U.S. Census Bureau, 2016, archiviert vom Original am 2018-08-19; abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Statistics Canada, 8. Mai 2013, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ a b c Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". United Nations, Department of Economic and Social Affairs, Population Division, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] INEGI, S. 1, archiviert vom Original am 2015-12-10; abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Dr. Claire M. Smith: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Overseas Vote Foundation, August 2010, archiviert vom Original am 2013-10-24; abgerufen am 9. September 2018: „Previous research indicates that the number of U.S. Americans living in Mexico is around 1 million, with 600,000 of those living in Mexico City.“
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Dezember 2005, archiviert vom Original am 2009-03-27; abgerufen am 17. April 2010 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Fundación UNAM, 28. August 2013, archiviert vom Original am 2018-09-10; abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CNN, 24. April 2013, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". El Sol de México, 25. März 2018, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Milenio, 5. Mai 2017, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". La Patilla, 19. Juli 2018, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". El Sol de México, 4. Dezember 2017, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". El Sol de México, 27. Juni 2018, abgerufen am 9. September 2018.
- ^ Graciela Olvera, Armando Martínez: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 25. Januar 2021, abgerufen am 25. März 2021 (spanish).
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Adherents.com, archiviert vom Original am 2007-11-12; abgerufen am 10. November 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". University of Michigan, 1997, archiviert vom Original am 2006-09-01; abgerufen am 3. Januar 2007.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Catholic Online, abgerufen am 24. Oktober 2011.
- ^ "Cristianismos orientales: persecución, muerte, migración y cambio – Resonancias – Instituto de Investigaciones Sociales", "UNAM", Mexico DF, 29 November 2019. Retrieved on 28 November 2020.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] 16. Juni 2009, archiviert vom Original am 2009-06-16.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".
- ^ Simons, Marlise (29 September 1979). "Mexico to End Work of U.S. Translators With Indians". The Washington Post.
- ^ Primack, Karen (1998). Jews in places you never thought of. KTAV Publishing House, Inc. p. 305. ISBN 978-0-88125-608-6.
- ^ Jacobo Grinberg Zylberbaum (1989). Los chamanes de México (University of Texas ed.). Mexico City: UNAM School of Psychology. ISBN 9686022015.
- ^ Castells Ballarin, Pilar (June 2008). "La Santa Muerte y la cultura de los derechos humanos". LiminaR. 6 (1): 13–25. doi:10.29043/liminar.v6i1.263.
- ^ Soto Laveaga, Gabriela. "Bringing the Revolution to| Medical School: Social Service and a Rural Health Emphasis." Mexican Studies/Estudios Mexicanos vol. 29 (2) summer 2013, 397–427.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Countrystudies.us, abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ a b Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Expatforum.com, abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Kwintessential.co.uk, archiviert vom Original am 2013-08-13; abgerufen am 4. November 2009.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Sinais.salud.gob.mx, archiviert vom Original am 2010-06-09; abgerufen am 30. Mai 2010.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Inegi.gob.mx, archiviert vom Original am 2011-07-22; abgerufen am 8. August 2011.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Inegi.gob.mx, archiviert vom Original am 2011-07-22; abgerufen am 8. August 2011.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Global Virtual University, archiviert vom Original am 2010-07-19; abgerufen am 2. Oktober 2007.
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".
- ^ Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 19. Juni 2019, abgerufen am 10. August 2019 (spanish).
- ^ "Recruiter's scoreboard Highlights" (PDF). The Wall Street Journal/Harris Interactive survey of corporate recruiters on business schools. Retrieved 4 October 2007.
- ^ Vasconcelos, José (1997). La Raza Cósmica (The Cosmic Race). Didier T. Jaén (translator). The Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 160. ISBN 978-0-8018-5655-6.
- ^ Phelan, John Leddy (1 August 1956). "México y lo Mexicano". Hispanic American Historical Review. 36 (3): 309–318. doi:10.1215/00182168-36.3.309. JSTOR 2509215.
- ^ Katzew, Ilona. Casta Painting: Images of Race in Eighteenth-Century Mexico. New Haven: Yale University Press 2005
- ^ Widdiefield, Stacie G. The Embodiment of the National in Late Nineteenth-Century Mexican Painting. Tucson: University of Arizona Press 1996
- ^ Anreus, Robin Adèle Greeley, and Leonard Folgarait, eds. Mexican Muralism: A Critical History. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press 2012.
- ^ Lozano, Luis-Martin, ed. Frida Kahlo: The Complete Paintings. Taschen 2021.ISBN 9783836574204
- ^ UNESCO World Heritage Centre: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Whc.unesco.org, 29. Juni 2007, abgerufen am 17. August 2013.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Archiviert vom Original am 2017-10-15; abgerufen am 15. Januar 2018.
- ^ Katherine Endicott: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 14. Oktober 2006, archiviert vom Original am 2011-09-19; abgerufen am 26. Juni 2009.
- ^ a b Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". CONACULTA, abgerufen am 27. September 2016.
- ^ University of Puget Sound: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] Archiviert vom Original am 2011-12-08.
- ^ La Crónica de Hoy: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] 20. September 2005, archiviert vom Original am 2012-10-23; abgerufen am 19. Januar 2018.
- ^ esmas.com: [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] 25. November 2005, archiviert vom Original am 2012-10-23.
- ^ Cocina, fiesta y cantos mexicanos reconocidos por UNESCO, El Universal (Mexico City) (newspaper), 16 November 2010
- ^ "Latina chef Daniela Soto-Innes is youngest to be named 'World's Best Female Chef'", NBC News, 26 April 2019, retrieved 12 July 2019
- ^ John Curl: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". In: Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". 20. August 2009, abgerufen am 14. Juli 2019.
- ^ a b González Echevarría, Roberto; Hill, Ruth, "Latin American literature", Encyclopaedia Britannica, retrieved 14 July 2019
- ^ Stevenson, Robert M. Music in Mexico: A Historical Survey. New York: Thomas Y. Crowell 1952
- ^ Russell, Craig. "Music: Mesoamerica through Seventeenth Century", Encyclopedia of Mexico, 976–980
- ^ Hess, Carol A. "Carlos Antonio de Padua Chávez y Ramírez", Encyclopedia of Mexico, 242–43
- ^ Zolov, Eric. "Counterculture", Encyclopedia of Mexico, 363–368
- ^ Zolov, Eric. Refried Elvis: The Rise of Mexican Counterculture. Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press 1999.
- ^ "An Introduction to the Ballet Folklórico de México".[17] accessed 15 May 2022
- ^ [18] [dead link] World Fact Book, Mexico. accessed 4 May 2022
- ^ Hanna Rosin, "Life Lessons: How Soap Operas Can Change the World", The New Yorker, 5 June 2006, pp. 40–45.
- ^ Soto Laveaga, Gabriela, "'Let's become fewer': Soap operas, contraception, and nationalizing the Mexican family in an overpopulated world." Sexuality Research and Social Policy. September 2007, vol. 4,, no. 3 pp. 19–33.
- ^ Dillingham, A.S. Oaxaca Resurgent: Indigeneity, Development, and Inequality in Twentieth-Century Mexico. Stanford: Stanford University Press 2021, 47–49, 69–70. ISBN 9781503627840
- ^ a b Baker, Shannon L. and William H. Beezley, "Sports", Encyclopedia of Mexico, 1370-1372
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] San Diego Metropolitan, Dezember 2003, archiviert vom Original am 2007-09-30; abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ [Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle". Script error: No such module "Vorlage:Internetquelle".] The Confederation of North, Central American and Caribbean Association Football (CONCACAF), archiviert vom Original am 2007-10-06; abgerufen am 7. Oktober 2007.
- ^ "México, una historia de éxito en la Serie Mundial de Ligas Menores" [Mexico, a history of success in the Minor League World Series], Medio Tiempo (in Spanish), 25 August 2010, retrieved 12 July 2019
- ^ "México es Campeón en el Mundial Sub-23 de beisbol" [Mexico is the World Baseball Champion in the Under-23 bracket], Medio Tiempo (in Spanish), 29 October 2018, retrieved 12 July 2019
- ^ "LOS TOROS EN MÉXICO" [Bullfighting in Mexico], Don Quijote (in Spanish), retrieved 11 July 2019
- ^ a b "Los mejores deportistas mexicanos de la historia" [The best Mexican athletes in history], Marca Claro (in Spanish), 12 October 2018, retrieved 11 July 2019
- ^ "Los medallistas que ha tenido el Box Olímpico mexicano" [The Mexican Olympic boxing medal winners], Caliente.mx (in Spanish), 15 August 2016, retrieved 11 July 2019
Further reading edit
- Anna, Timothy. Forging Mexico, 1821-1835. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press 1998.
- Adams, Richard E.W. Prehispanic Mesoamerica. 3rd. ed. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press 2005.
- Beezley, William H., ed. A Companion to Mexican History and Culture. Blackwell 2011. ISBN 9781405190572
- Bulmer-Thomas, Victor, John H. Coatsworth, and Roberto Cortés Conde, eds. The Cambridge Economic History of Latin America. Vol. 1, The Colonial Era and the Short Nineteenth Century. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 2006.
- Camp, Roderic Ai. Politics in Mexico: Democratic Consolidation or Decline? (Oxford University Press, 2014)
- Coerver, Don M., Suzanne B. Pasztor, and Robert M. Buffington. Mexico: An Encyclopedia of Contemporary Culture and History. Santa Barbara: ABCClio 2004. ISBN 1-57607-132-4
- Davis, Diane. Urban Leviathan: Mexico City in the Twentieth Century (Temple University Press, 2010)
- Hale, Charles A. The Transformation of Mexican Liberalism in Late Nineteenth-Century Mexico. Princeton: Princeton University Press 1989.
- Hamnett, Brian R. Roots of Insurgency: Mexican Regions 1750-1824. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1985.
- Kirkwood, Burton. The History of Mexico (Greenwood, 2000) online edition
- Knight, Alan. The Mexican Revolution. 2 vols. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1986.
- Krauze, Enrique (1998). Mexico: Biography of Power: A history of Modern Mexico 1810–1996. New York: Harper Perennial. p. 896. ISBN 978-0-06-092917-6.
- Levy, Santiago. Good intentions, bad outcomes: Social policy, informality, and economic growth in Mexico (Brookings Institution Press, 2010).
- Merrill, Tim and Ramón Miró. Mexico: a country study (Library of Congress. Federal Research Division, 1996) US government document; not copyright online free
- Meyer, Michael C.; Beezley, William H., eds. (2000). The Oxford History of Mexico. Oxford University Press. p. 736. ISBN 978-0-19-511228-3.
- Meyer, Michael C., William L. Sherman, and Susan M. Deeds. The Course of Mexican History (7th ed.) (Oxford University Press, 2002) online edition
- Rugeley, Terry. Epic Mexico: A History from Earliest Times. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press 2020. ISBN 9780806167077
- Van Young, Eric. Stormy Passage: Mexico from Colony to Republic, 1750-1850. Lanham MD: Rowman and Littlefield 2022. ISBN 9781442209015
- Vinson, Ben, III. Before Mestizaje: The Frontiers of Race and Caste in Colonial Mexico. New York: Cambridge University Press 2018.
- Werner, Michael S. ed. Encyclopedia of Mexico: History, Society & Culture (2 vol 1997) 1440pp online edition
- Werner, Michael S. (January 2001). Concise Encyclopedia of Mexico. Taylor & Francis. ISBN 978-1-57958-337-8.
External links edit
Government
- The Government of Mexico
- VisitMexico.com – Official tourism website (Archived 3 August 2022 at the Wayback Machine)
General information
- The World Factbook. Central Intelligence Agency. Mexico.
- U.S. Agency for International Development. Mexico.[permanent dead link]
- U.S.-Mexico foreign trade balance. Mexico.
- Mexico from BBC News
- Mexico at Encyclopædia Britannica
- Wikimedia Atlas of Mexico
- Key Development Forecasts for Mexico from International Futures
Template:Mexico topics Template:World Heritage Sites in Mexico